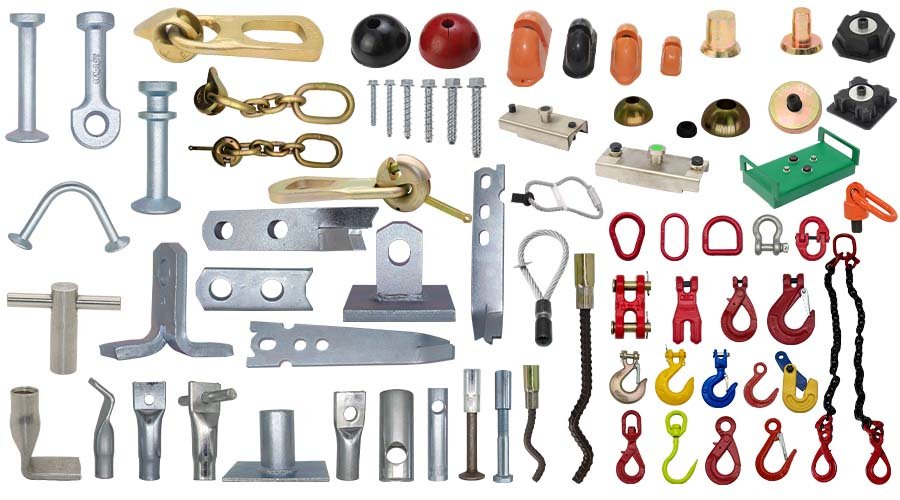
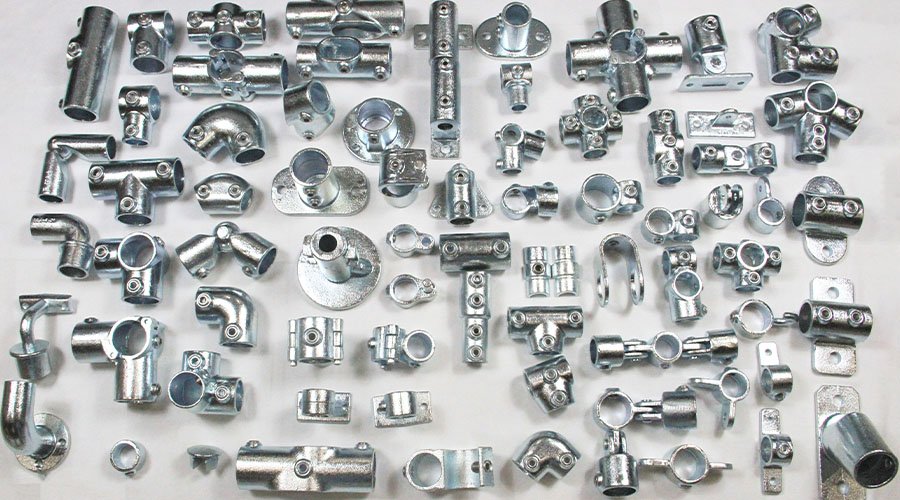
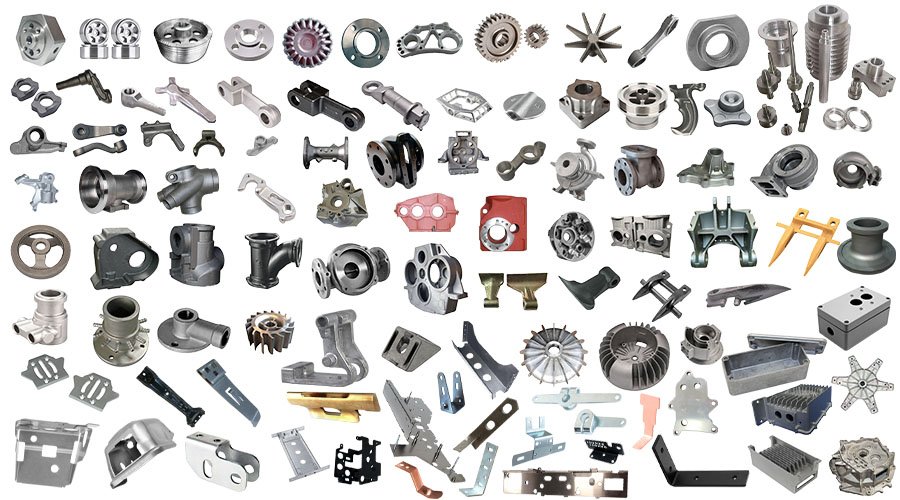
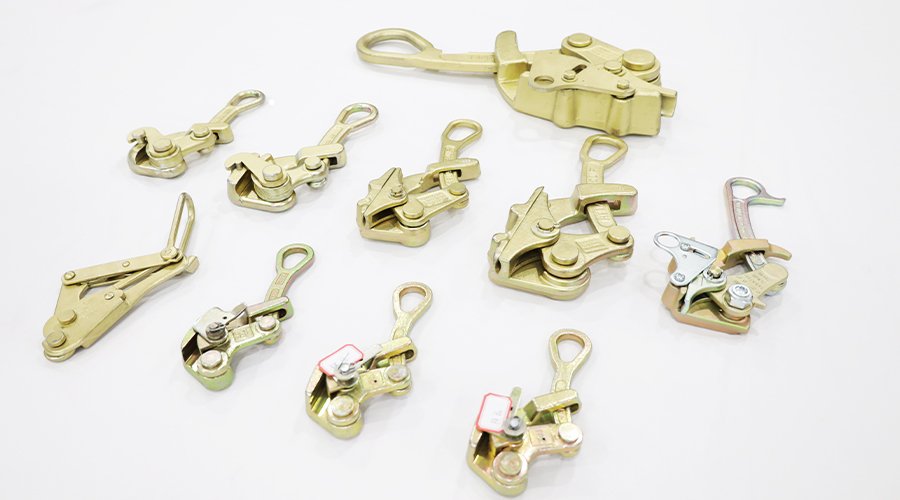
Custom pump and valve components, including impellers, housings, shafts, seals, and valve bodies, are tailored to meet specific flow control, pressure, and environmental requirements. Designed for sectors like oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing, these parts enhance system efficiency and reliability through accurate manufacturing and robust material selection.

 EN
EN RU
RU