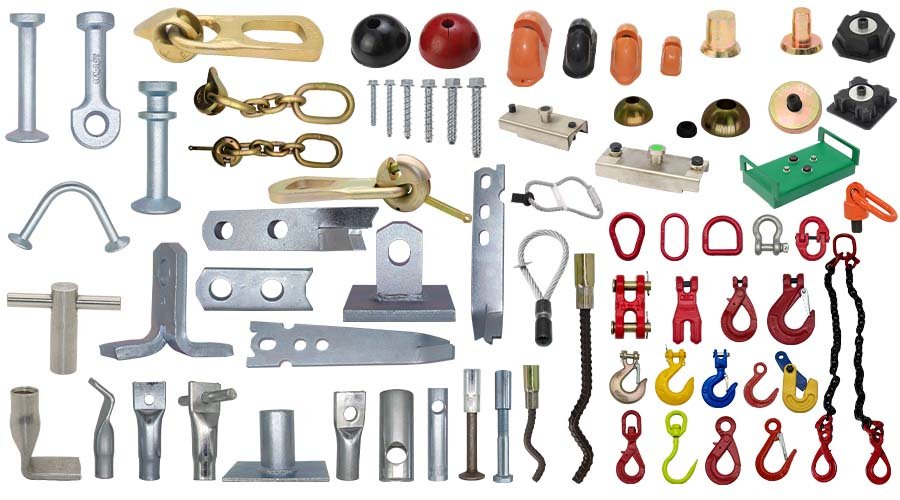
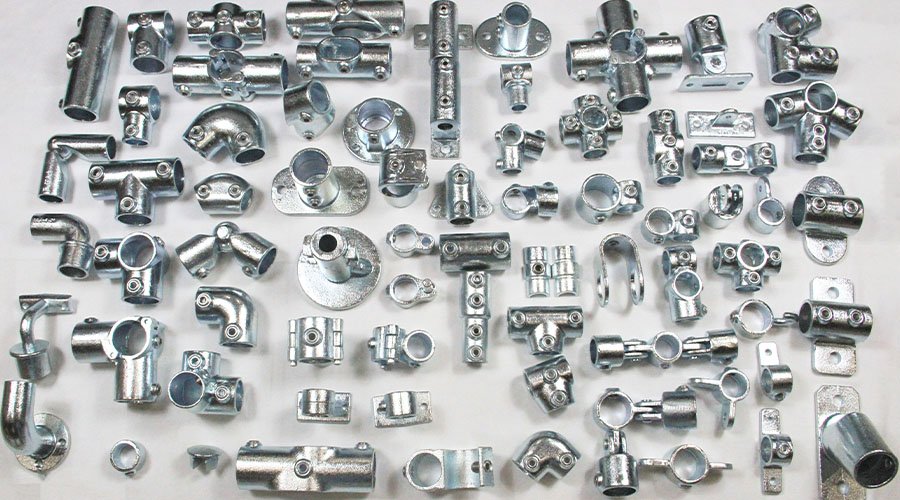
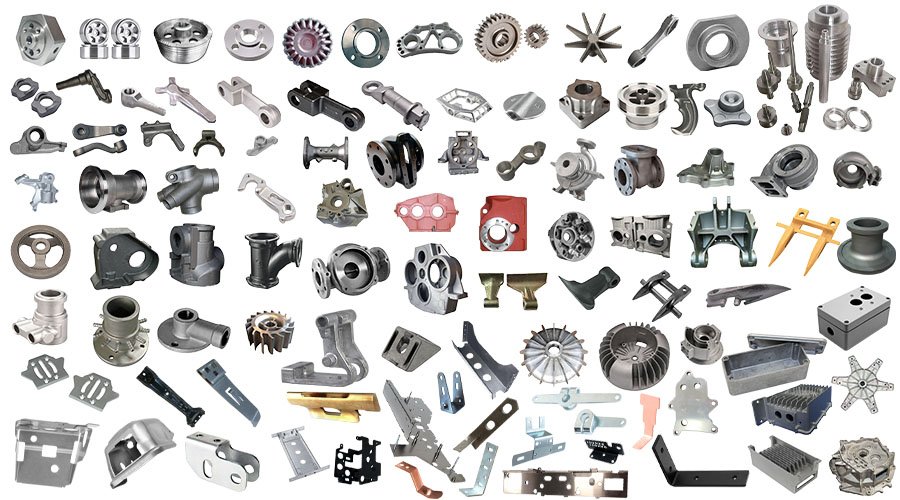
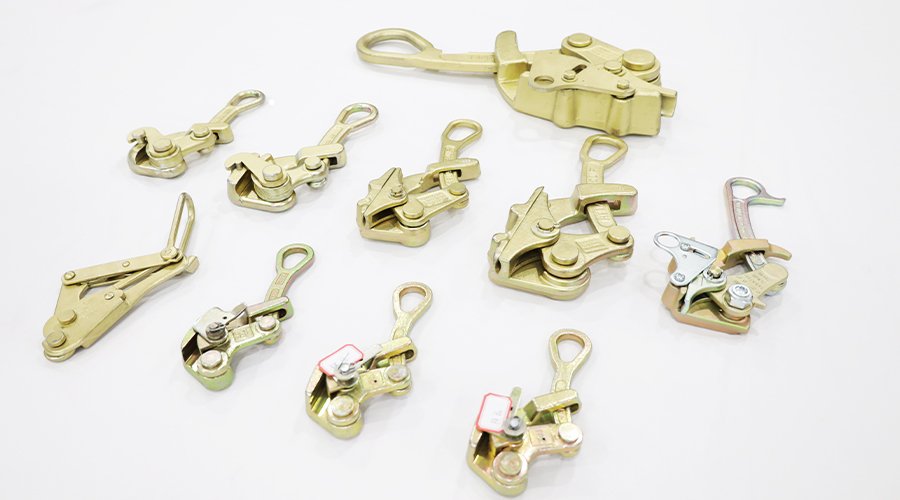
Custom cast iron parts are available in various shapes and specifications to suit demanding applications. Popular products include manhole covers, pipe fittings, pump housings, gear wheels, and counterweights. Each part is engineered for exceptional strength, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy. Whether for heavy machinery, infrastructure projects, or decorative architecture, our cast iron components meet exact design requirements and deliver consistent performance in even the toughest environments.

 EN
EN RU
RU