Our tensile limit inspection tests the maximum pull strength of magnets, ensuring stable fixation under heavy load conditions and preventing displacement during casting and curing.

Precast magnetic formers supplied by HULK Metal use permanent magnets with stronger magnetic force and longer service life. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a professional team to provide better services and better products. We strictly implement ISO 9001 management, and precast magnetic formers can have higher quality.










1. ISO 9001Certification
2. QA Services
3. Save More Money
4. Various Precast magnetic Formers
HULK Metal can provide a variety of precast magnetic formers. With higher quality and more affordable price, it is your best choice.
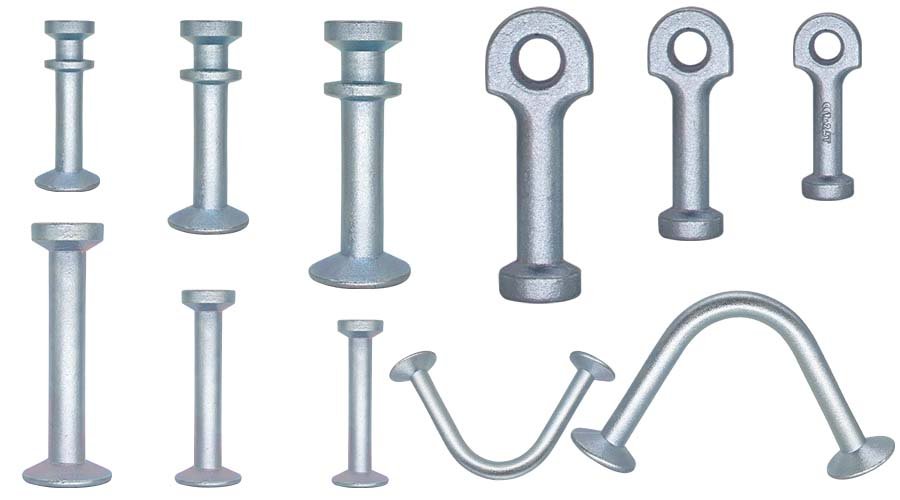
Precast Magnetic Formers have various styles, including fixed Precast Frame, Lifting Anchors Sockets and Spread Anchors. You can download our product catalog.
| Type | What It Is | How They Work | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precast Magnetic Formers for Lifting Anchor | Magnetic steel moulds designed to create recesses for lifting anchors in precast concrete elements. | The magnets hold the former securely to the steel formwork, accurately shaping the anchor pocket during concrete casting. | Used in beams, slabs, and panels to allow lifting anchor installation for safe transportation and placement. |
| Precast Magnetic Formers for Spread Anchor | Specially shaped magnetic formers that produce recesses for spread anchors, which distribute lifting loads. | Magnets fix the former to the mould without drilling, ensuring precise alignment and preventing movement during vibration. | Common in large precast wall panels, staircases, and structural elements requiring even load distribution during lifting. |
| Precast Magnetic Formers for Lifting Socket | Cylindrical or conical magnetic moulds used to form pockets for lifting sockets in concrete. | The magnetic base attaches to the mould surface, creating a clean recess for socket placement after curing. | Ideal for elements requiring threaded lifting sockets, such as façade panels and utility structures. |
| Precast Magnetic Formers for Corrugated Tube | Magnetic holders designed to form and fix corrugated tubes in position before concrete pouring. | Magnets keep the former aligned with the mould wall, holding the corrugated tube securely during vibration. | Used in post-tensioning ducts, cable pathways, and embedded conduit systems in precast components. |
| Precast Magnetic Formers for Electrical Junction Box | Magnetic moulds that create recesses for embedding electrical junction boxes in concrete. | The magnetic former attaches to the steel formwork, shaping an exact cavity for the box while preventing displacement. | Suitable for architectural panels, wall panels, and precast units needing built-in electrical access points. |
Precast Magnetic Formers provide stronger magnetic fixation for precast frames and accessories on steel plates, enhancing efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Precast Magnetic Formers are specially designed construction magnets that utilize magnetic attraction to secure precast frames and precast concrete accessories onto iron or steel plates. By offering stronger holding force compared to mechanical fasteners, they stabilize formwork components more reliably during the casting process. Their user-friendly design allows contractors to position and reposition formers more flexibly, reducing installation time and minimizing labor costs. Ideal for a variety of precast concrete applications, these magnetic formers enhance on-site safety by eliminating loose hardware. Engineered for durability, they deliver longer service life under demanding production environments, making them a superior alternative for modern precast concrete fabrication.
Each Precast Magnetic Former consists of two primary components: a high-strength magnet core and an outer casing material selected based on functional requirements. The magnet is manufactured from premium rare-earth alloys to achieve stronger magnetic attraction, ensuring more reliable grip on steel plate surfaces even under heavy load conditions. Surrounding the magnet, the external shell can be customized using iron, rubber, plastic, or composite materials. An iron casing enhances durability in abrasive environments, making it more resistant to wear during repetitive mounting and demounting. Rubber coatings provide a softer interface against fragile surfaces, reducing the risk of marring paint or delicate finishes. Meanwhile, plastic housings offer corrosion-resistant properties, making them more suitable for wetter or chemically aggressive conditions. In some applications, composite materials combine the advantages of multiple substrates, yielding a more versatile solution for diverse production scenarios.
The design of the outer casing also accounts for ergonomic handling and safety. Larger units feature molded grips that are more comfortable for operators to maneuver, while smaller formers can be streamlined for use in tight spaces between reinforcing bars. Each casing is precision-machined to fit the magnet core snugly, preventing unwanted movement that could compromise magnetic force. Some models even integrate indicator labels or molded protrusions to help workers align formers more quickly, speeding up installation.
Internally, the magnet core undergoes a specialized magnetization process that makes its magnetic field orientation stronger and more uniform. This consistent magnetic flux ensures that each former provides more predictable performance across its entire surface area. To protect the magnet from corrosion and mechanical impact, the core is often sealed inside the casing with industrial-grade adhesives or resin. The combined effect of these design choices leads to Precast Magnetic Formers that are not only stronger and more durable than conventional alternatives but also more adaptable to various precast concrete accessory types and production workflows, effectively positioning them as a more efficient choice for modern precast fabrication.
Precast Magnetic Formers enable more versatile placement of precast frames and accessories, streamlining production across diverse concrete components and industries.
Precast magnetic formers offer a stronger, more flexible solution for securing precast concrete panel frames to steel foundations. By simply positioning the magnetic formers at each frame connection, installers eliminate the need to use bolts or clamps, which reduces installation time. This approach is particularly useful on large precast jobs where more consistent alignment is critical to ensure panels remain level and stable throughout the pouring and curing phases.
Precast Magnetic Formers simplify the installation of lifting pins by holding them securely during the concrete casting process. Workers place the lifting pins in designated recesses on the form panel and then attach a magnetic former behind the steel template. Compared to mechanical fasteners, these magnetic mounts offer faster placement and repositioning, making them ideal for high-volume production where minimizing cycle time is more critical.
For spread anchors used in connecting precast elements, Precast Magnetic Formers offer a more efficient attachment method. The magnetic formers hold the anchor plates firmly against the steel forming bed, preventing misalignment during concrete placement. This reduces the risk of anchor displacement, leading to more accurate alignment of embedded hardware. As a result, installers experience fewer adjustments and faster turnaround, improving overall fabrication throughput.
Precast sockets require precise positioning to ensure compatibility with service conduits and structural connections. By using Precast Magnetic Formers, manufacturers can attach socket frames more rapidly than traditional mechanical brackets. A magnetic former placed on the steel bedplate holds the socket housing at the exact location, ensuring it stays in place during casting. This more dependable fixation reduces defects and scrap, optimizing production yield.
When embedding electric socket boxes within precast panels, Precast Magnetic Formers enable more reliable placement against steel templates. The magnetic force maintains constant contact, preventing unwanted shifts as concrete is poured. This results in cleaner cutouts and more accurate integration of electrical fixtures. Since formers can be lifted and repositioned easily, electricians and mold technicians achieve faster cycle times and reduce rework, enhancing project profitability.
Metal corrugated pipe sleeves embedded in precast concrete benefit from the consistent holding strength of Precast Magnetic Formers. By affixing a magnetic former behind the corrugated pipe template, installers ensure that the sleeve remains stationary throughout casting. This prevents deformation or displacement caused by concrete pressure. The easier removal of formers after cure also minimizes damage to the corrugated pipe, ensuring better alignment for post-installation plumbing or wiring.
Compared to standard Recess Formers, Precast Magnetic Formers offer more mobility, durability, ease of use, and application versatility overall.
Unlike ordinary Recess Formers that require bolts or screws to secure them and remain fixed, Precast Magnetic Formers can be freely mounted and repositioned on the steel bedplate. This more flexible approach eliminates the need for drilling or additional hardware, enabling workers to adjust form placement more quickly. The result is a more efficient workflow where form adjustments happen faster and with less effort.
Because Precast Magnetic Formers use premium rare-earth magnets sealed within protective casings, they exhibit a longer service life compared to standard Recess Formers that rely on mechanical parts prone to wear. Over time, mechanical fasteners may loosen, bend, or corrode, leading to more frequent replacements. By contrast, magnetic formers resist abrasion and corrosion more effectively, delivering a more durable solution that reduces overall maintenance costs.
Installation and removal become simpler with Precast Magnetic Formers since workers only need to place or lift the formers without handling nuts, bolts, or wrenches. This more straightforward process reduces the number of tools required on-site and minimizes the risk of losing small hardware components. The result is faster setup and teardown time, allowing teams to allocate labor toward other value-added tasks instead.
Precast Magnetic Formers provide more flexible application scenarios because they can adapt to different precast concrete designs without custom drilling patterns. Contractors can use the same magnetic formers to fabricate various panel types, from wall segments to architectural facades, without modifying existing molds. This versatility streamlines tool inventory and simplifies production planning, making it more cost-effective for manufacturers handling multiple precast product lines.
Although Precast Magnetic Formers come with a higher price tag than traditional Recess Formers, the total lifecycle cost can be more favorable due to fewer replacements and lower labor expenses. The initial investment in magnetic formers pays off through reduced downtime, less maintenance, and faster production cycles. For high-volume operations, the improved productivity often offsets the premium cost, delivering more value over time.
Precast Magnetic Formers use magnetic adhesion to hold form components in place during casting, streamlining placement and removal steps consistently.
First, the frame of the precast concrete element is positioned on a steel plate base, ensuring it aligns with the production layout. Workers check the frame orientation, making sure each edge meets the required design tolerance. The steel bedplate must be clean and flat so the magnetic formers can adhere more securely, preventing any misalignment during the subsequent attachment process.
Next, operators place different types of Precast Magnetic Formers at designated locations on the steel bedplate, based on the accessory or frame recess required. Each former should be matched to its respective function—whether securing lifting inserts, anchors, or conduit sleeves—to ensure more precise positioning. Technicians verify that the magnets are flush against the plate to maximize holding force and prevent movement under load.
Then, concrete is carefully poured into the formwork, covering the frame and accessories held by magnetic formers. During this pouring stage, the magnetic pull remains strong, preventing formers and embedded items from shifting under the weight of wet concrete. As workers vibrate and level the mixture, the magnetic formers help maintain the correct geometry, resulting in more consistent surface finish and structural integrity.
After concrete reaches sufficient strength, typically following a predetermined curing time, the Precast Magnetic Formers are removed. Operators simply pull each former away from the steel surface, releasing the embedded accessory with minimal effort. Because the magnetic attachment eliminates mechanical fasteners, removal is straightforward and causes less surface damage. The formers can then be cleaned and re-magnetized if necessary for the next casting cycle.
Production of Precast Magnetic Formers involves precise magnet shaping, custom casing fabrication, careful assembly, and rigorous quality testing processes.
The production process begins with manufacturing magnets of specified shapes using high-grade rare-earth material. Magnet blanks are cut and machined into the desired geometry, such as blocks, discs, or custom profiles for unique form supports. Each magnet undergoes a demagnetization and remagnetization cycle to ensure its magnetic flux is oriented correctly. Surface treatments may also be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and durability under damp conditions.
Next, specialized outer casing components are produced according to functional requirements. Depending on the application, casings may be molded from plastic, rubber, iron, or composite blends. CNC machining, injection molding, or stamping techniques are employed to achieve precise dimensions that match the magnet core. Functional features such as gripping handles, alignment guides, and protective bumpers are incorporated to make the final product more user-friendly and more versatile on-site.
During assembly, magnets are carefully inserted into their respective casings, ensuring a snug fit that prevents internal movement. Industrial-grade adhesives or resins are used to bond the magnet to the housing, creating a unified structure. Workers also install any necessary gaskets, handles, or alignment markers at this stage. Each unit is visually inspected for proper assembly, with more attention paid to bonding quality and external finish to guarantee more consistent performance.
Finally, each Precast Magnetic Former undergoes a comprehensive testing procedure. Magnet strength is measured using gauss meters or pull-test devices to confirm optimal holding force. Dimensional checks ensure that each former matches design specifications. Additionally, environmental testing, such as salt-spray or temperature cycling, may be performed to verify corrosion resistance and durability. Only units that pass all tests receive a detailed quality report before being packed for shipment.
At our Precast Magnetic Formers Quality Control Center, we employ advanced testing instruments to ensure each unit meets stringent performance benchmarks. We measure magnetic pull strength, verify dimensional accuracy, and inspect the integrity of the protective casing. Through rigorous random sampling, we maintain a pass rate exceeding 99%. Each batch of formers is accompanied by a detailed inspection report summarizing key metrics and test results. In addition to our robust QA procedures, we offer comprehensive after-sales service. If any product exhibits quality issues or arrives with insufficient quantity, customers can request returns, exchanges, or replenishments. Our commitment to superior quality control guarantees more reliable formers and more consistent production outcomes.
At our Precast Magnetic Formers Quality Control Center, we employ advanced testing instruments to ensure each unit meets stringent performance benchmarks. We measure magnetic pull strength, verify dimensional accuracy, and inspect the integrity of the protective casing. Through rigorous random sampling, we maintain a pass rate exceeding 99%. Each batch of formers is accompanied by a detailed inspection report summarizing key metrics and test results. In addition to our robust QA procedures, we offer comprehensive after-sales service. If any product exhibits quality issues or arrives with insufficient quantity, customers can request returns, exchanges, or replenishments. Our commitment to superior quality control guarantees more reliable formers and more consistent production outcomes.
Our tensile limit inspection tests the maximum pull strength of magnets, ensuring stable fixation under heavy load conditions and preventing displacement during casting and curing.
We verify every Precast Magnetic Former against design drawings with precision measuring tools, ensuring accurate dimensions for stable installation and consistent performance in precast concrete production.
We check hole positions and diameters with specialized gauges to ensure correct fitment of anchors, sockets, and conduits, reducing installation errors and improving precast product accuracy.
Before delivery, our QA team inspects each batch for appearance, performance, and strength, ensuring customers receive defect-free Precast Magnetic Formers ready for immediate use.
Each shipment undergoes strict quantity checks, with packaging verified against orders to guarantee customers receive the correct number of precast magnetic formers without shortages or errors.
HULK Metal operates multiple specialized factories to provide one-stop production of Precast Magnetic Formers. From raw magnet shaping to surface treatment and final inspection, every step is supported by advanced equipment and skilled technicians. Our complete supply chain and coordinated production allow us to deliver higher quality products faster. By combining strong manufacturing capabilities with ISO 9001 management, we ensure more reliable performance and more competitive prices for global customers.
Our dedicated QC Center is equipped with pull testers, salt-spray chambers, and precision gauges to verify each Precast Magnetic Former’s performance. Every unit undergoes dimensional checks, magnetic force testing, and durability evaluation before packaging. Random sampling and detailed reports ensure each batch meets ISO 9001 standards. In case of any defects, our after-sales team provides fast solutions through replacement or replenishment. This strict quality management system guarantees more reliable products and higher customer satisfaction in precast concrete projects.
At our surface treatment factory, Precast Magnetic Formers receive customized finishes to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Options include powder coating, rubber coating, zinc plating, or specialized anti-rust treatments depending on customer needs. Each treatment improves resistance against moisture, abrasion, and chemical exposure, extending the product’s service life. With automated lines and strict process control, we deliver consistent, high-quality surface finishes. Customers benefit from more reliable products that withstand demanding precast production environments worldwide.
Our production factory is equipped with advanced CNC machines, stamping presses, and injection molding lines for manufacturing magnet cores and customized casings. Skilled technicians oversee every step, ensuring precise assembly and durability. By integrating magnet processing, casing fabrication, and adhesive bonding in one site, we shorten lead times and improve production stability. This efficient setup enables HULK Metal to supply Precast Magnetic Formers in bulk while maintaining high accuracy, consistency, and performance across all orders.
Choosing HULK Metal's Precast Magnetic Formers delivers more value through streamlined procurement, faster production, and enhanced quality assurance globally.

With HULK Metal's one-stop purchasing model, customers benefit from more simplified procurement of Precast Magnetic Formers and related precast accessories. Instead of sourcing magnets, casings, and hardware from multiple vendors, clients can place a single order directly with HULK Metal, which consolidates all components into a unified supply chain. This more integrated approach reduces administrative overhead and shipping complexity. By leveraging HULK Metal's extensive supplier network and material sourcing capabilities, customers gain more reliable access to high-quality magnetics and casings, which translates into more consistent production schedules and fewer supply disruptions. Overall, our streamlined procurement system leads to more efficient project planning and more predictable project costs.

HULK Metal's Precast Magnetic Formers are manufactured under an ISO 9001 certified quality management system, offering customers more assurance in product consistency and performance. The ISO certification reflects our commitment to more rigorous process controls, standardized operating procedures, and continuous improvement. From raw material inspection to final shipment, every step adheres to internationally recognized quality standards. Compliance with ISO 9001 reduces the risk of defects and ensures more reliable magnetic strength and dimensional accuracy. By choosing an ISO-certified supplier, customers experience more confidence in the reliability of their precast magnetic formers and benefit from more consistent outcomes in their construction projects.

By integrating HULK Metal Precast Magnetic Formers into their production line, manufacturers conserve more time and energy. The quick magnetic attachment reduces manual labor compared to bolting or clamping systems, streamlining the setup and removal of formings. This more user-friendly process decreases worker fatigue and boosts safety by minimizing handling of small hardware. As a result, production cycles become shorter, allowing companies to handle more orders in less time. This more efficient energy and labor utilization free up resources for other core business activities, enhancing overall operational productivity.

Investing in HULK Metal Precast Magnetic Formers delivers more cost savings over the long term. Although our magnetic formers may have a higher initial price point, their longer lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements result in lower total cost of ownership. Clients spend less on replacement formers and spare mechanical fasteners. Additionally, faster installation and removal translate into labor savings and less downtime on the production floor. This more efficient workflow reduces material waste and decreases rework, ultimately contributing to more profitable precast concrete operations.

HULK Metal's optimized production processes and well-coordinated logistics offer more expedited delivery timelines for Precast Magnetic Formers. By maintaining closer partnerships with raw material suppliers and operating multiple manufacturing facilities, we reduce lead times compared to competitors. Our production workflows and inventory management systems are more agile, allowing us to scale output quickly based on customer demand. Advanced order tracking and dedicated customer service teams keep clients informed at each stage, ensuring more transparent communication. As a result, manufacturers receive their magnetic formers sooner, minimizing downtime and accelerating precast concrete project schedules.
To help our customers gain a deeper understanding of Precast Magnetic Formers and their applications, we provide a range of related articles. These cover topics such as installation guidance, comparison with traditional recess formers, maintenance tips, and innovative applications in precast concrete production. Each article offers practical knowledge to assist engineers, procurement managers, and construction professionals in selecting the right products. By accessing these resources, customers can improve their project efficiency and make more informed purchasing decisions.
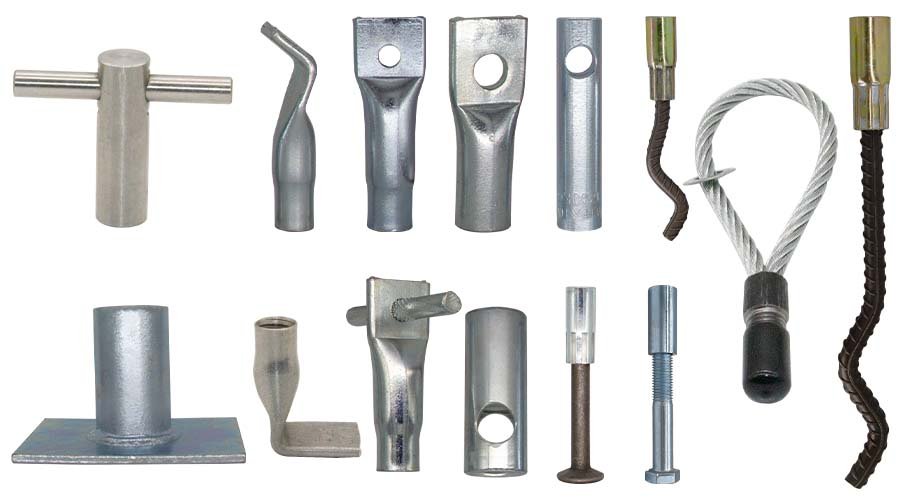
In addition to Precast Magnetic Formers, HULK Metal also supplies a wide range of precast concrete accessories. These include lifting anchors, spread anchors, wire rope loops, shuttering magnets, recess formers, and corrugated pipes. All products are manufactured under ISO 9001 standards and supported by strict quality control. With a complete supply chain and one-stop purchasing service, we help customers reduce sourcing costs, improve production efficiency, and ensure reliable performance across different precast concrete projects worldwide.

Precast concrete lifting anchors are accessories designed specifically for the lifting of precast concrete elements. It includes lifting pin anchors (as know as dog bone anchors, spherical head lifting anchors), double head lifting anchors, utility anchors, etc. It needs to be embedded in precast concrete elements, fixed with a recess former, and a recess is created in the fixed position to accommodate the lifting clutch. They can be used in many elements such as: concrete trenches, culverts, stairs, pipes, panels, etc.

Lifting & Fixing Sockets, also commonly called Lifting & Fixing Inserts, are accessories designed for the lifting and anchoring of precast concrete elements. They are pre-buried in specific locations in the concrete to provide lifting points or connection holes for lifting or connecting other elements. With the development of the quick-install concrete industry, many types have been derived. It generally consists of two parts: a sleeve part and a stress transfer part. Depending on the different stress transfer parts, dozens of products can be derived.

Precast concrete spread anchors are made of high-performance alloy steel plates and are designed to be embedded in precast concrete elements to provide accessories for lifting points. Its international standard is CE certification. It needs to undergo strict tensile performance sampling inspection—using a tensile force of 3 times or even higher safety factor until it is broken. There are many types of it, and when using it, you need to consider the shape, thickness, lifting point location, weight and other factors of the precast concrete elements.

HULK Metal has been engaged in the production and sales of precast concrete lifting clutch since 2006, and has accumulated rich experience. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a professional team to provide better products and services. Our lifting clutch has passed the CE certification and can pass the destructive test with a 5-fold safety factor. Here you can learn about our product range, production capacity, and service capabilities.
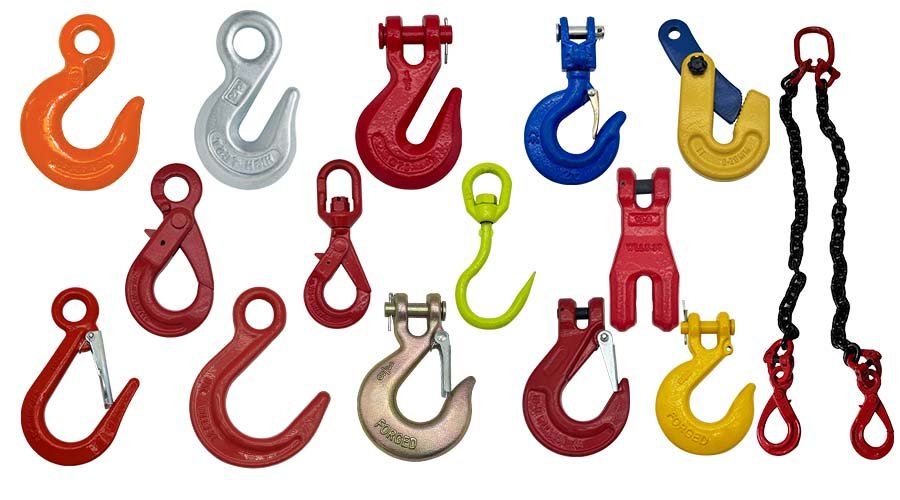

HULK Metal offers a wide range of G60, G70, and G80 strength lifting hooks with a well-established supply chain. We have an advanced forging factory and integrated assembly line production. The quality of lifting hooks will be more guaranteed, and we can provide electro-galvanizing, hot-dip galvanizing, and powder coating—three surface treatments. We strictly implement ISO 9001 standard management to provide you with higher quality products and services. You can contact us at any time to visit the factory to understand our production capacity and service capabilities, and then hand over the order to us after you are satisfied.

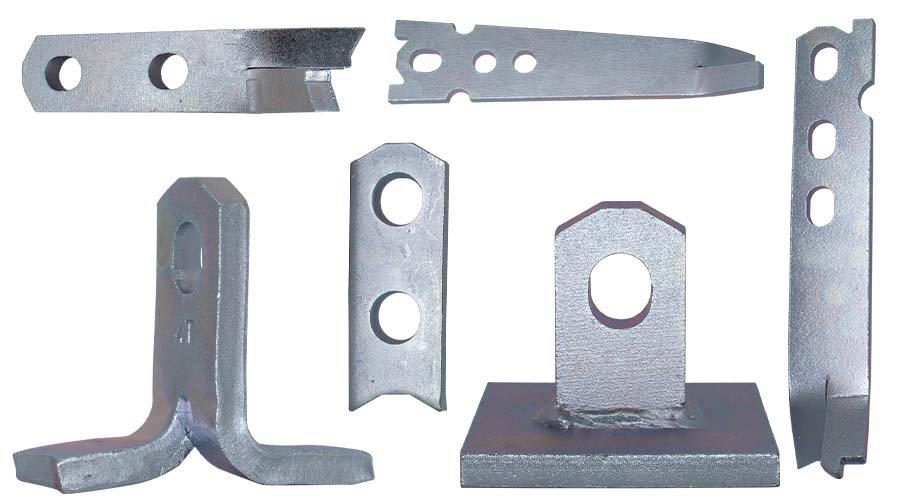
Recess formers are used to place lifting anchors, spread anchors, and other accessories that need to be pre-buried in precast concrete elements. The recess they leave is for the lifting clutch to connect with lifting anchors or spread anchors. We offer a full range of standard recess formers and OEM services for special requirements.
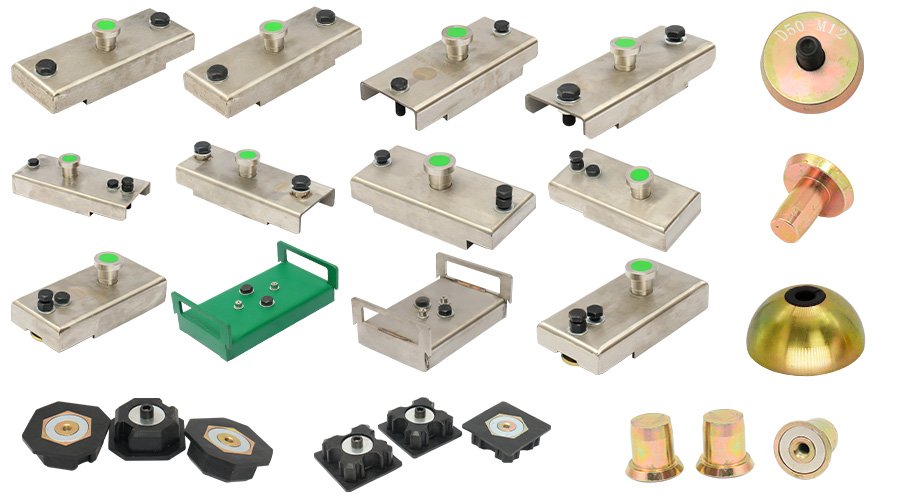

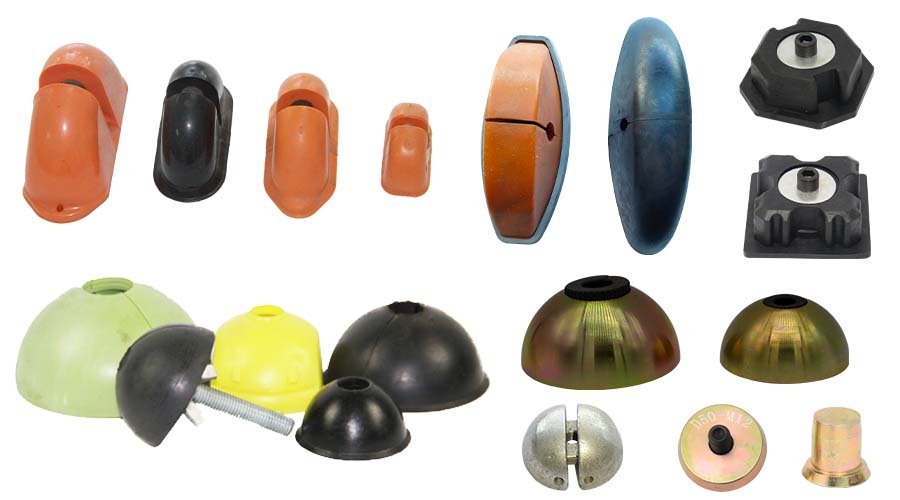
Precast concrete magnets are one of HULK Metal's main products. They are recognized by customers for their high quality and reasonable price. Precast concrete magnets use high-performance and durable NdFeB alloy magnets. Advanced technology effectively improves production efficiency and reduces costs while ensuring its quality. We provide quality assurance services. You can purchase them with confidence.
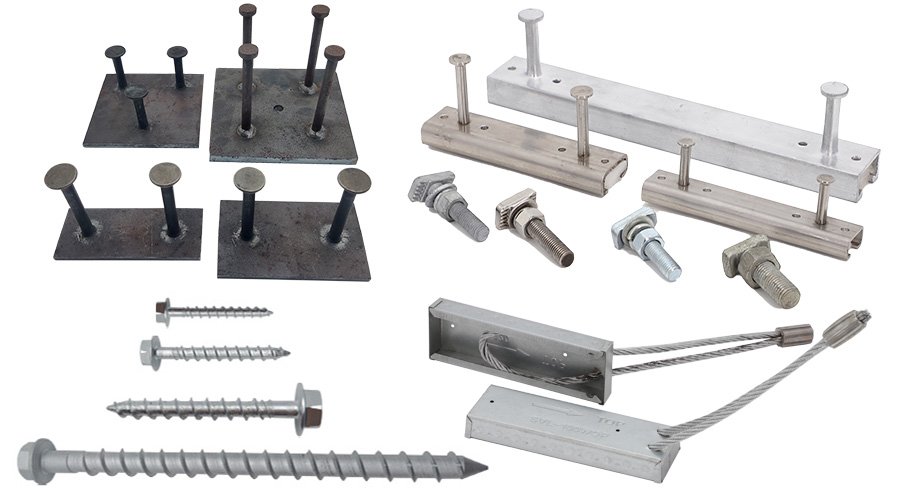

HULK Metal also specializes in OEM services for cast-in-channel, T-bolts, wire rope boxes, stone support brackets, and other accessories. Cast in channel can be made of cold-rolled steel, hot-rolled steel, and stainless steel. T bolts are made of carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. Our wire rope box only has one wire rope, and stone support brackets only accept OEM services. We will develop a perfect solution according to your requirements to ensure that the delivery time, quality, and price can meet your requirements.
HULK Metal offers high-quality foot anchors designed for secure lifting of precast concrete elements. Our CE and ISO 9001 certified lifting pin anchors ensure a threefold safety factor, shorter production cycles, and prompt delivery.
HULK Metal has supplied tens of millions of Lifting Pin Anchors ranging from 1.3 tons to 32 tons to hundreds of buyers around the world. We have a full range of products and a complete supply chain to provide you with quality services. We provide quality assurance services. Please feel free to inquire.
HULK Metal manufactures lifting pin (dog bone) anchors with higher standards to meet demanding precast concrete lifting needs. We offer complete OEM solutions, from design and production to surface treatment and delivery, ensuring each anchor provides excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with various lifting systems.
HULK Metal stands out as a leading manufacturer of lifting eye anchors, specializing in precast concrete lifting eye anchors that meet stringent CE certification with a 3 times safety factor.
Durable precast concrete double head lifting pin anchors from HULK Metal ensure secure lifting, higher safety factors, and corrosion resistance, meeting CE and ISO 9001 standards for demanding construction applications worldwide.
Durable, CE-certified spherical head lifting anchors from HULK Metal offer reliable load capacity and corrosion resistance, ensuring safe, efficient lifting for precast concrete projects with fast delivery and quality assurance.
Lifting Pins for Precast Concrete supplied by HULK Metal are CE certified. We can supply Lifting Pins that can pass the tensile test of 3 times the safety factor and strictly implement the IS0 9001 standard to provide high-quality services.
Short Wavy Tail Anchor is a compact, high-strength lifting solution for precast concrete elements. Its wavy rebar tail ensures even load distribution, prevents concrete cracking, and connects securely with threaded sockets or lifting inserts for safe, efficient operations.
Wavy tail anchor is made of high-performance steel pipe and rebar extrusion after bending. Its SWL range is between 0.5 and 8.0 tons. There are two thread standards, M and RD.
HULK Metal is a well-known supplier in China, providing high-quality and cost-effective Precast Lifting Thread Insert. With a complete supply chain and a professional team, we have provided flat end insert, solid rod insert, Tubular insert and others to global customers. We provide complete QA services. Looking Forward Your Inquiry.
HULK Metal is one of the high-quality Flat End Lifting Insert suppliers in China. In order to provide better services and products, we have integrated a complete supply chain. We strictly implement ISO 9001 management, and after years of development, we can now supply a full range of CE certified Flat End Lifting Insert.
Solid Rod Lifting Inserts supplied by HULK Metal have passed the CE certification. They can pass the tensile test with 3 times the safety factor. We strictly implement ISO 9001 standards to manage the entire supply chain to ensure that we can provide you with better Solid Rod Lifting Inserts and services.
Solid rod lifting and fixing sockets embed into precast concrete for secure threaded connections. Crafted from sturdy steel rods, one end features tapping for attachments, while the other includes a hole for rebar passage, enhancing structural integrity.
The combi lifting socket combines a lifting pin anchor and threaded socket, providing a strong, secure connection for lifting and handling precast concrete elements in construction and infrastructure projects.
HULK Metal's Flat End Fixing Socket with Cross Pin integrates a robust cross bar to improve load stability. Manufactured to CE and ISO 9001 standards, it ensures exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and reliability for various precast concrete lifting applications.
Fixing sockets with bent ends, also known as fixing inserts with bent ends, is essential for anchoring in precast concrete. These sockets provide robust points for fixing elements, featuring a bent design that enhances grip and stability.
Tubular Lifting Insert supplied by HULK Metal has passed CE certification. Tubular Lifting Insert can pass the 3 times safety factor tensile test, and each batch of goods has a comprehensive test report.
HULK Metal can provide you with RD and M standard 12-45 thread, SWL 0.5 to 8.0tons of Long Wavy Lifting Insert. Its international general standard is CE, which needs to pass the 3 times safety factor tensile force test.
HULK Metal manufactures durable solid rod fixing sockets with cross pins and inserts with cross bars for precast concrete. CE and ISO 9001 certified, with high safety factors and quick delivery for bulk orders.
HULK Metal offers premium flat end lifting sockets designed for safe and efficient handling of precast concrete elements. Manufactured from high-strength alloy steel and certified to CE and ISO 9001 standards, these lifting inserts provide exceptional load capacity and corrosion resistance.
HULK Metal's tubular lifting sockets, made from high-grade steel or stainless steel, provide secure threaded connections in precast concrete. CE certified and precision manufactured, they ensure reliable lifting performance, excellent durability, and meet strict safety requirements for diverse construction applications.
The Long Wavy Lifting Socket combines a threaded steel pipe with a wavy-tail rebar to achieve deeper stress transfer in precast concrete. Designed for heavy-duty lifting, it meets CE and ISO 9001 standards and ensures a 4 times safety factor.
Q345/20#/Stainless steel/Others
Galvanized/Black
8~52
≥3
Flat plate lifting sockets embed into precast concrete for secure lifting points. The design includes a threaded end for clutch attachment and a broad base for load distribution, available in galvanized finishes for added durability.
Flat end fixing sockets, also known as flat end fixing inserts, anchor securely into precast concrete for fixing. Made from sturdy steel, they feature a flat end for easy installation and a threaded interior for bolts.
Plate spread anchors from HULK Metal feature a welded steel plate and head design, embedded in concrete for edge lifting. Available in various sizes with galvanized options, they support loads up to 10 tons safely.
Unilateral erection anchors serve as specialized lifting inserts for precast concrete, designed for one-sided loading during element erection. They integrate with ring clutches and recess formers, providing stable anchor points that enhance safety and reduce panel stress in construction applications.
HULK Metal supplies flat foot anchors crafted from premium alloys for secure lifting in precast concrete projects worldwide.
HULK Metal stands as a reliable erection anchor supplier in China, delivering high-standard products for precast concrete lifting. Our anchors ensure secure handling with superior strength and corrosion resistance, backed by comprehensive production support for bulk orders.
HULK Metal supplies CE and ISO9001 certified spread anchors with reliable safety factors, faster delivery, and professional support. Choose our spread anchors for superior quality and complete precast lifting solutions.
HULK Metal delivers high-quality two-hole anchors, designed for secure lifting of precast concrete elements. Certified with CE and ISO 9001, our anchors ensure safety, durability, and efficiency.
This page presents comprehensive information about precast concrete lifting clutches, including types, structure, materials, production processes, surface treatment options, applications, quality control standards, supplier selection guidance, and factory capabilities.
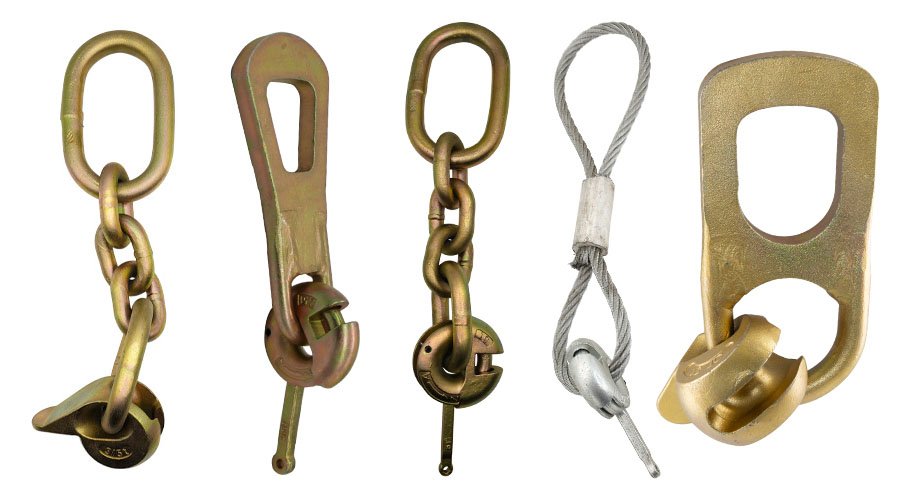
Ring Clutch supplied by HULK Metal is CE certified and can pass the tensile test with a safety factor of 5. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a complete team to provide better products and services.
HULK Metal's Precast Concrete Lifting Lugs, also known as Lifting Clutches or Lifting Eyes, are precision-engineered for heavy-duty lifting. Manufactured with high-strength materials, they ensure safety, durability, and efficiency in precast concrete lifting applications worldwide.
High-quality dog bone lifting eye with CE and ISO9001 certification. Strong, safe, and durable for precast concrete lifting. Shorter production cycle and faster delivery from trusted Chinese supplier HULK Metal.
HULK Metal supplies CE and ISO 9001 certified lifting clutch for pin anchor with 5 times safety factors, shorter production cycles, and complete after-sales support for global precast concrete projects.
Dog Bone Lifting Eye With Chain supplied by HULK Metal can pass the 5 times safety factor test and has been CE certified. We can provide 1.3 to 20 tons load groups.
Ring Clutch supplied by HULK Metal is CE certified and can pass the tensile test with a safety factor of 5. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a complete team to provide better products and services.
Precast Concrete Lifting Eyes supplied by HULK Metal has passed CE and ISO 9001 Certified and can passed 5 times safety factor testing. HULK Metal is an experienced manufacturer in China. Looking forward your inquire.
Q345/35CrMo/Others
Galvanized/Black/Powder-coat
1.3~32.0
≥5
Precision Casting
HULK Metal has a well-established supply chain to provide you with a full range of Clevis Slip Hooks, such as G43, G70, G80, CE marked, with latch or none, electro-galvanized, hot-dip galvanized or powder coated.
We have provided customers in more than 100 countries and regions around the world with Clevis Grab Hooks with strength standards such as G43 70 80 that can pass 2 to 4 Times Safety Factor detection.
HULK Metal is an experienced eye grab hooks supplier in China. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a professional team to provide better products and services. We can provide eye grab hooks with various specifications and surface treatments.
HULK Metal is an experienced supplier in China, providing Eye Slip Hooks in various materials, strengths, certifications, surface treatments and sizes. We have established a complete supply chain to ensure that raw materials, production and delivery are under control to provide higher quality and low-cost lifting hooks.
Anchor Recess is an essential component for positioning lifting anchors accurately in precast concrete elements. HULK Metal supplies Anchor Recess in multiple materials and configurations to match different lifting systems and production methods.
HULK Metal provides high-quality Rubber Recess Former for precast concrete lifting systems. They are used with Pin Anchor Recess Former and Spread Anchor Recess Former, ensuring precise recess shaping, shorter production cycles, and faster delivery.
HULK Metal supplies durable lifting pin anchor recess former for precast concrete elements, offering sizes from 1.3 to 32 tons with CE and ISO 9001 certification. Get shorter cycles and comprehensive support for bulk orders.
HULK Metal can provide a variety of precast magnetic formers. With higher quality and a more affordable price, it is your best choice.
The Spread Anchor Rubber Recess Former is made of durable rubber with a reinforced rear metal plate. It is designed for fixing spread anchors in precast concrete, ensuring accurate positioning, easy demolding, and reliable lifting performance.
As one of the excellent magnetic recess former suppliers in China, HULK Metal has advanced factories and perfect supply chain to provide you with high-quality products and services.
HULK Metal can provide CE-certified magnets for precast lifting and fixing inserts or sockets. Our factory has advanced machining equipment, laser cutting machines, and assembly lines, which can more efficiently complete CE-certified precast lifting fixing insert socket magnet with a higher pass rate.
HULK Metal's Electrical Box Fixed Magnets feature a durable rubber body combined with strong NdFeB magnets, ensuring reliable fixation of electrical boxes in precast concrete. These magnets are customizable in shape, size, and finish, providing flexibility for bulk orders.
Our Shuttering Magnets for Formwork are designed for precast concrete production, offering reusable and stable fixing solutions. They support different mold sizes and deliver better cost-efficiency for large-scale construction projects.
Our Embedded Corrugated Pipe Fixed Magnet combines premium steel housing with powerful magnets to ensure strong fixation during precast concrete production. It reduces installation time, improves efficiency, and provides consistent performance across different applications, helping customers achieve safer and more reliable concrete elements.
Steel Embed Plates are essential components used to create strong, reliable connection points within precast concrete structures. As an experienced manufacturer in China, HULK Metal supplies Concrete Embed Plates with stable quality, flexible customization, and consistent production capacity.
Cast In Channel T Bolts from HULK Metal are precision-forged using high-performance alloy steel or stainless steel. Surface treatments, including electro-galvanizing or hot-dip galvanizing, enhance rust resistance, making them reliable for precast concrete connections in construction and infrastructure projects.
HALFEN Anchor Channels from HULK Metal offer superior quality, CE and ISO certified standards, and five times safety factor. Our fast production and delivery, combined with professional after-sales support, make bulk purchasing simple and reliable.
Name Wire Loop Box Precast Concrete Accessories
Molds Full Range Moulds
Materials Wire Rope / Steel Plate / Customized
SL(mm)±10 60 / 80 / 100 / 120 /140
Our Cast in Channel offers superior strength, certified safety, and flexible application for precast construction. Manufactured with advanced processes, it guarantees durability, easier installation, and faster delivery. HULK Metal supports bulk buyers with full technical service and reliable after-sales support.
Our concrete screw bolts are designed for reliable installation without expansion anchors. Galvanized concrete screws provide superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for indoor and outdoor use. HULK Metal offers diverse sizes, surface treatments, and customized solutions to match your needs.
Q345/20#/Stainless steel/Others
Galvanized
0.8~25.0
6~32
≥3
HULK Metal lifting loops are made from alloy or carbon steel, precision-threaded, and electro-galvanized for corrosion resistance. Designed for use with lifting sockets, they ensure safe, reliable handling of precast concrete components with a ≥4 safety factor.

As a top metalworking service provider, we want to let every customer experience a sense of security in purchasing, sales, etc., and better realize their value through continuously defining new standards for products and services.
Room 901, Intelligent Park A Building, No. 86 ChunYang Rd, Qingdao, China 266109
© 2025 HULK Metal All Rights Reserved. All Rights Reserved.








 EN
EN RU
RU