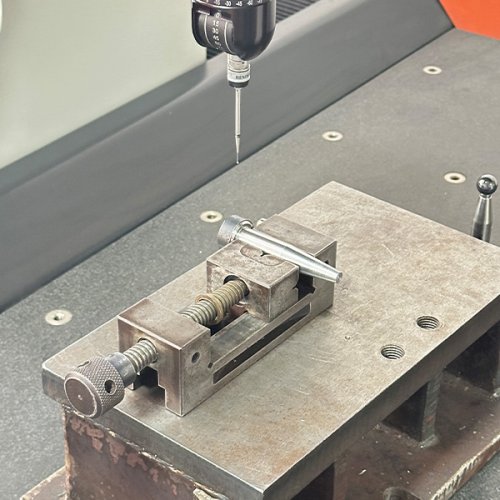
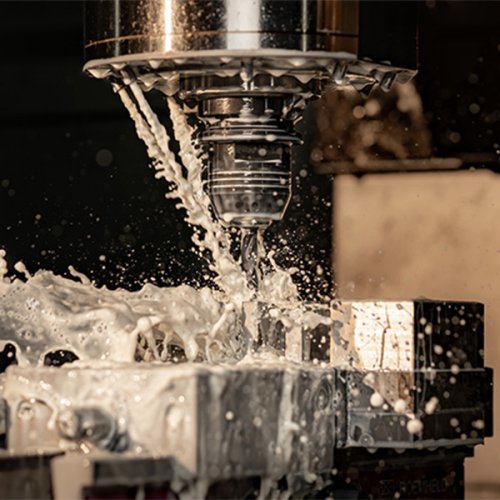
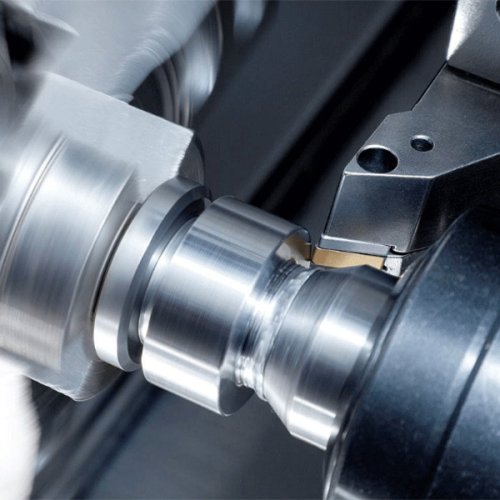
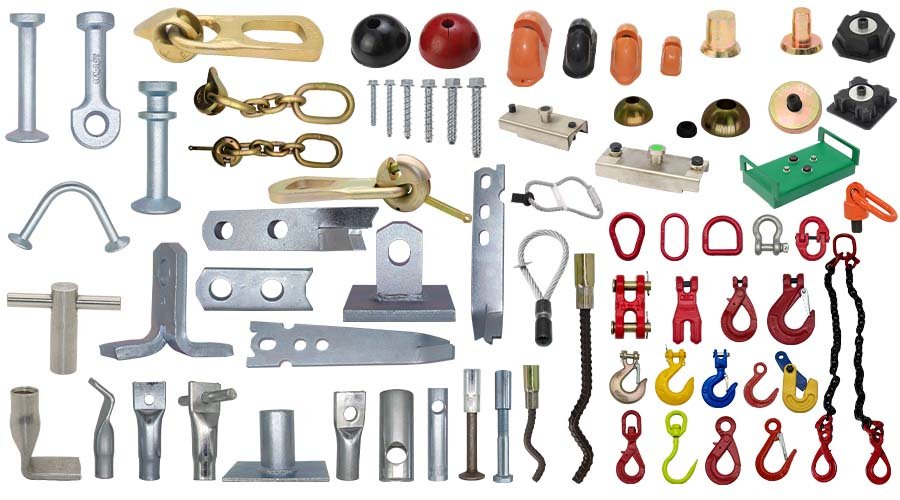
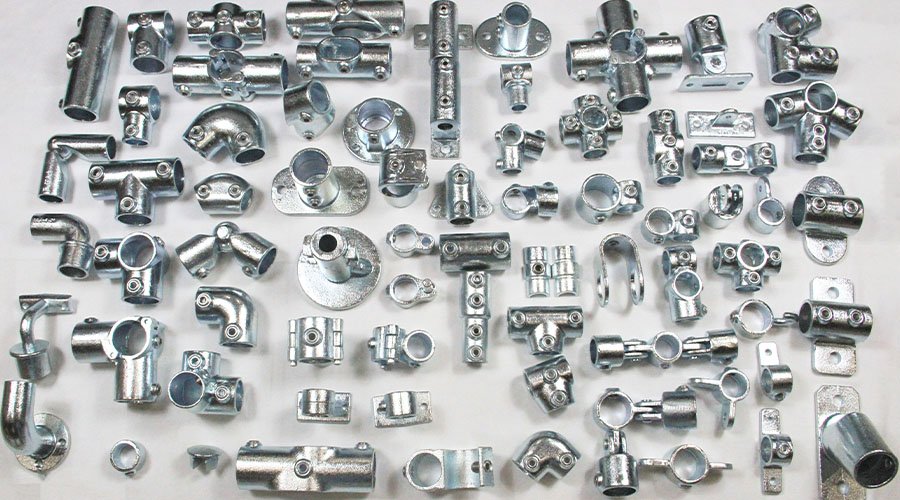
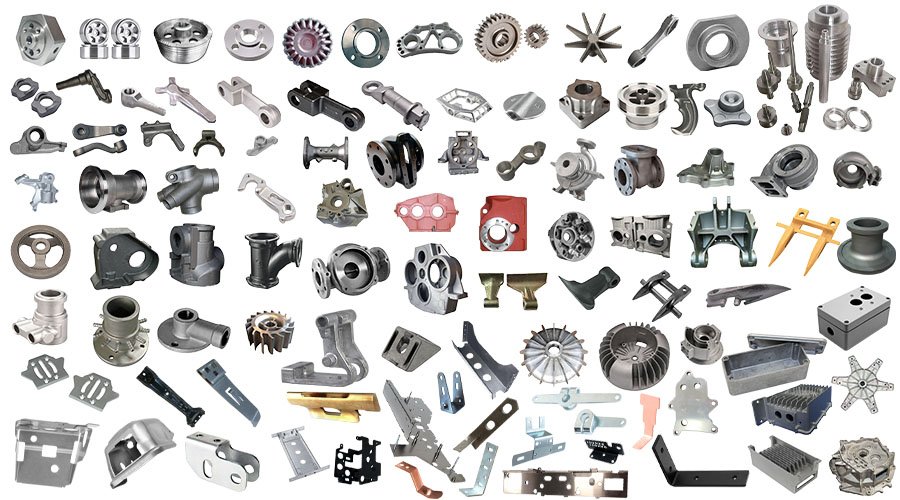
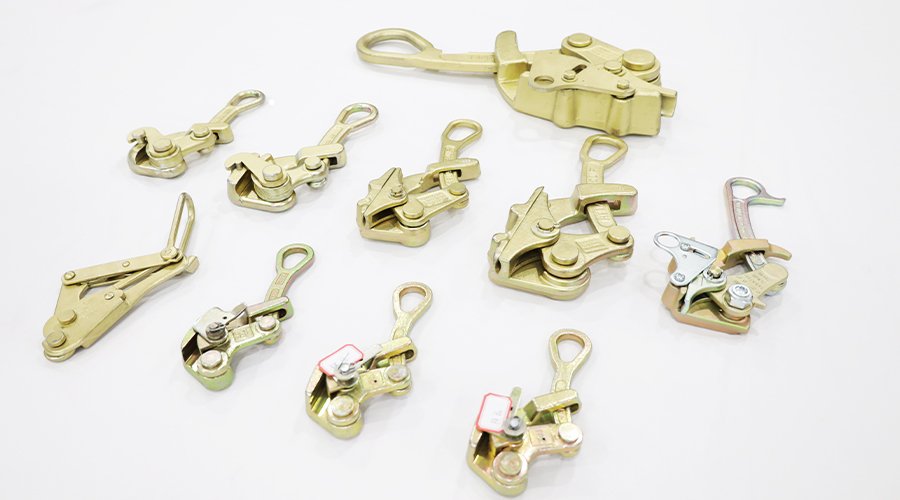
We specialize in producing a wide range of CNC machining parts, including turned, milled, and custom components made from aluminum, steel, titanium, and plastics. Each part is manufactured with micron-level precision to fit diverse applications in automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial equipment.

 EN
EN RU
RU