We supply various stamping dies including blanking dies, bending dies, drawing dies, compound molds, and progressive dies, suitable for processing carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper in different production scenarios.

HULK Metal has answered many questions that have been recognized by customers. We have collected these questions and answers. You can see them here. If you don't see what you want here, you can contact us directly.
Selecting the right die according to the stamping parts is one of the key steps in stamping production, because the die directly affects product quality, production efficiency and cost control. This article will explain in detail how to choose the right die from multiple angles.
Select a blanking die or a composite die.
The die must have high precision to ensure that the cut is smooth and the size is accurate.
The wear resistance of the blade is high, and carbide or high-speed steel can be selected.
Select a bending die or a flanging die.
The shape of the die should match the bending angle and size.
The material's rebound resilience should be considered and the appropriate amount of bending should be designed.
Drawing die.
The die should have good finish to reduce the friction of the material during the drawing process.
Select an appropriate blank holder to prevent wrinkling or cracking.
Calculate the drawing coefficient to avoid material deformation beyond the limit.
Choose a forming mold or a multi-station continuous mold.
The mold structure is complex and the material fluidity needs to be considered.
High-precision mold processing ensures shape and details.
Choose a progressive mold or a compound mold.
Complete multiple processes in one set of molds.
The mold must meet the matching accuracy of multiple stations and is suitable for mass production.
Moderate hardness and good wear resistance of the mold edge.
The mold material can be Cr12 or Cr12MoV.
Stainless steel has high hardness and strength, and the mold needs to have high strength and wear resistance.
It is recommended to choose carbide or high-alloy tool steel as the mold material.
Pay attention to lubrication during processing to avoid adhesion between the material and the mold.
Aluminum is soft and easy to deform. The mold surface should be smooth to reduce material scratches.
Wear-resistant steels such as SKD11 or DC53 can be used.
Copper is soft but easy to oxidize, so the mold needs to be smooth and corrosion-resistant.
Use high-finish mold steel or nitriding surface treatment.
simple mold, such as single-process mold.
Low manufacturing cost and simple design.
Applicable to scenes with low part complexity and small processing volume.
progressive die or continuous die.
Can complete multiple processes at the same time with high efficiency.
The manufacturing cost is high, but it can be amortized to the cost per piece, suitable for long-term use.
The mold structure needs to be strong and can withstand the processing pressure of large-area materials.
Large punching machines are matched with molds to ensure the stability of processing.
Step-by-step mold or large drawing die.
Mold-cutting edges and cavities must have high processing accuracy.
The matching clearance must be precise, and a guide pin and guide sleeve structure must be used.
High-precision molds, such as continuous molds for electronic products.
Ensure that the tonnage of the mold matches that of the press to avoid poor workpiece forming due to insufficient pressure or mold damage due to excessive pressure.
Mechanical press: suitable for high-speed stamping and simple-shaped parts.
Hydraulic press: suitable for processes such as drawing and bending that require stable pressure.
CNC punch press: suitable for mass production of complex-shaped parts.
Choose the mold type according to the project budget. For example:
Ordinary molds can be used for small batches.
Long-life molds are preferred for large batches.
Mold materials with high strength and high wear resistance are suitable for mass production.
For experimental or short-term production, mold materials with lower costs can be selected.
Determine the cycle of mold processing and debugging, and select a mold solution suitable for the project delivery date.
large size, complex curved surface, and high precision requirements.
Mold selection: Use large drawing die and multi-station mold.
Ensure dimensional accuracy while reducing labor costs.
The mold needs to be durable to meet the needs of mass production.
small size, high precision, and thin material.
Mold selection: high-precision progressive die.
Continuous processing process to reduce production cycle.
The mold edge needs to be smooth to avoid material scratches.
medium size, bending and punching combination.
Mold selection: combination mold or compound mold.
Improve production efficiency and reduce mold adjustment time.
Complete punching and bending processes at one time.
Choosing the right mold for stamping parts is a multi-dimensional decision-making process, which requires comprehensive consideration of process requirements, material properties, production batch, dimensional accuracy, equipment conditions, and economy. Reasonable mold selection can not only ensure the quality of stamping parts, but also greatly improve production efficiency and reduce manufacturing costs. This is one of the core steps to achieve efficient production and enhance competitiveness.
Custom stamping die selection, material matching, and process optimization services help you achieve higher product quality, lower production costs, and shorter lead times. Ideal for both small batch trials and high-volume manufacturing projects.
HULK Metal offers premium hot die forging services to help you manufacture high-strength, complex-shaped metal parts with excellent surface quality. We specialize in forging gears, flanges, connecting rods, and other custom components for industries like construction, mining, automotive, and machinery. Backed by top-tier forging equipment, skilled technicians, and a strict quality control system, we ensure precision and consistency at scale. From drawing review to final delivery, our team provides full support to help you streamline your supply chain and get more competitive in your market.
We supply various stamping dies including blanking dies, bending dies, drawing dies, compound molds, and progressive dies, suitable for processing carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper in different production scenarios.
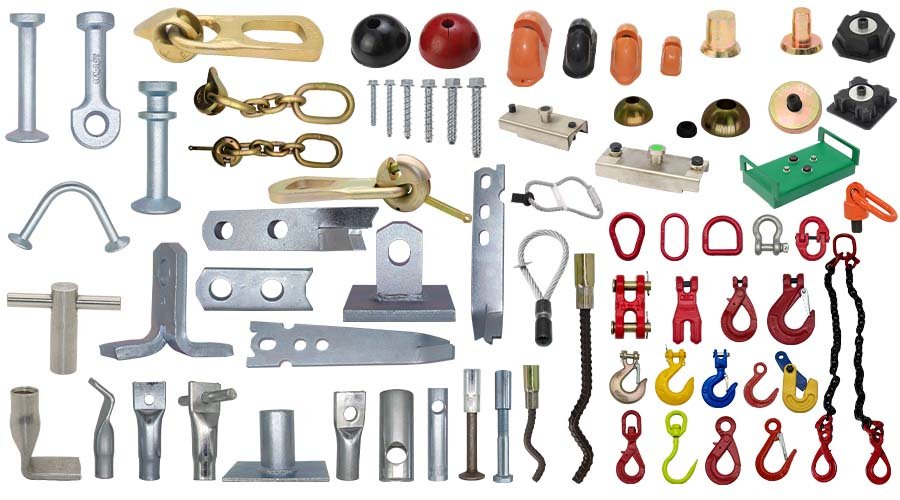

Precast concrete accessories are designed for precast concrete elements lifting, transport, fixing and connection. It includes those buried in concrete to provide lifting points, such as lifting anchors, sockets, spread anchors, and so on; those used to connect lifting points and lifting equipment, such as lifting clutch, hooks, loops, hoist rings; those used to connect other elements or fix other objects, such as wire rope box, cast in channel and others.
HULK Metal has been supplying precast concrete accessories from China to customers around the world since 2006. We have integrated a complete supply chain and built an experienced team to provide higher quality products and services. We can currently provide CE certified precast concrete lifting anchors, sockets (inserts), spread anchors, clutch, hooks, hoist rings, cast in channel, wire rope box, recess former, and others. We will strictly implement ISO 9001 standards for every order you make and provide QA services to make your purchase worry-free.

Precast concrete lifting anchors are accessories designed specifically for the lifting of precast concrete elements. It includes lifting pin anchors (as know as dog bone anchors, spherical head lifting anchors), double head lifting anchors, utility anchors, etc. It needs to be embedded in precast concrete elements, fixed with a recess former, and a recess is created in the fixed position to accommodate the lifting clutch. They can be used in many elements such as: concrete trenches, culverts, stairs, pipes, panels, etc.
HULK Metal offers high-quality foot anchors designed for secure lifting of precast concrete elements. Our CE and ISO 9001 certified lifting pin anchors ensure a threefold safety factor, shorter production cycles, and prompt delivery.
HULK Metal has supplied tens of millions of Lifting Pin Anchors ranging from 1.3 tons to 32 tons to hundreds of buyers around the world. We have a full range of products and a complete supply chain to provide you with quality services. We provide quality assurance services. Please feel free to inquire.
HULK Metal manufactures lifting pin (dog bone) anchors with higher standards to meet demanding precast concrete lifting needs. We offer complete OEM solutions, from design and production to surface treatment and delivery, ensuring each anchor provides excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with various lifting systems.
HULK Metal stands out as a leading manufacturer of lifting eye anchors, specializing in precast concrete lifting eye anchors that meet stringent CE certification with a 3 times safety factor.
Durable precast concrete double head lifting pin anchors from HULK Metal ensure secure lifting, higher safety factors, and corrosion resistance, meeting CE and ISO 9001 standards for demanding construction applications worldwide.
Durable, CE-certified spherical head lifting anchors from HULK Metal offer reliable load capacity and corrosion resistance, ensuring safe, efficient lifting for precast concrete projects with fast delivery and quality assurance.
Lifting Pins for Precast Concrete supplied by HULK Metal are CE certified. We can supply Lifting Pins that can pass the tensile test of 3 times the safety factor and strictly implement the IS0 9001 standard to provide high-quality services.

Lifting & Fixing Sockets, also commonly called Lifting & Fixing Inserts, are accessories designed for the lifting and anchoring of precast concrete elements. They are pre-buried in specific locations in the concrete to provide lifting points or connection holes for lifting or connecting other elements. With the development of the quick-install concrete industry, many types have been derived. It generally consists of two parts: a sleeve part and a stress transfer part. Depending on the different stress transfer parts, dozens of products can be derived.
Short Wavy Tail Anchor is a compact, high-strength lifting solution for precast concrete elements. Its wavy rebar tail ensures even load distribution, prevents concrete cracking, and connects securely with threaded sockets or lifting inserts for safe, efficient operations.
Wavy tail anchor is made of high-performance steel pipe and rebar extrusion after bending. Its SWL range is between 0.5 and 8.0 tons. There are two thread standards, M and RD.
HULK Metal is a well-known supplier in China, providing high-quality and cost-effective Precast Lifting Thread Insert. With a complete supply chain and a professional team, we have provided flat end insert, solid rod insert, Tubular insert and others to global customers. We provide complete QA services. Looking Forward Your Inquiry.
HULK Metal is one of the high-quality Flat End Lifting Insert suppliers in China. In order to provide better services and products, we have integrated a complete supply chain. We strictly implement ISO 9001 management, and after years of development, we can now supply a full range of CE certified Flat End Lifting Insert.
Solid Rod Lifting Inserts supplied by HULK Metal have passed the CE certification. They can pass the tensile test with 3 times the safety factor. We strictly implement ISO 9001 standards to manage the entire supply chain to ensure that we can provide you with better Solid Rod Lifting Inserts and services.
Solid rod lifting and fixing sockets embed into precast concrete for secure threaded connections. Crafted from sturdy steel rods, one end features tapping for attachments, while the other includes a hole for rebar passage, enhancing structural integrity.
The combi lifting socket combines a lifting pin anchor and threaded socket, providing a strong, secure connection for lifting and handling precast concrete elements in construction and infrastructure projects.
HULK Metal's Flat End Fixing Socket with Cross Pin integrates a robust cross bar to improve load stability. Manufactured to CE and ISO 9001 standards, it ensures exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and reliability for various precast concrete lifting applications.
Fixing sockets with bent ends, also known as fixing inserts with bent ends, is essential for anchoring in precast concrete. These sockets provide robust points for fixing elements, featuring a bent design that enhances grip and stability.
Tubular Lifting Insert supplied by HULK Metal has passed CE certification. Tubular Lifting Insert can pass the 3 times safety factor tensile test, and each batch of goods has a comprehensive test report.
HULK Metal can provide you with RD and M standard 12-45 thread, SWL 0.5 to 8.0tons of Long Wavy Lifting Insert. Its international general standard is CE, which needs to pass the 3 times safety factor tensile force test.
HULK Metal manufactures durable solid rod fixing sockets with cross pins and inserts with cross bars for precast concrete. CE and ISO 9001 certified, with high safety factors and quick delivery for bulk orders.
HULK Metal offers premium flat end lifting sockets designed for safe and efficient handling of precast concrete elements. Manufactured from high-strength alloy steel and certified to CE and ISO 9001 standards, these lifting inserts provide exceptional load capacity and corrosion resistance.
HULK Metal's tubular lifting sockets, made from high-grade steel or stainless steel, provide secure threaded connections in precast concrete. CE certified and precision manufactured, they ensure reliable lifting performance, excellent durability, and meet strict safety requirements for diverse construction applications.
The Long Wavy Lifting Socket combines a threaded steel pipe with a wavy-tail rebar to achieve deeper stress transfer in precast concrete. Designed for heavy-duty lifting, it meets CE and ISO 9001 standards and ensures a 4 times safety factor.
Q345/20#/Stainless steel/Others
Galvanized/Black
8~52
≥3
Flat plate lifting sockets embed into precast concrete for secure lifting points. The design includes a threaded end for clutch attachment and a broad base for load distribution, available in galvanized finishes for added durability.
Flat end fixing sockets, also known as flat end fixing inserts, anchor securely into precast concrete for fixing. Made from sturdy steel, they feature a flat end for easy installation and a threaded interior for bolts.

Precast concrete spread anchors are made of high-performance alloy steel plates and are designed to be embedded in precast concrete elements to provide accessories for lifting points. Its international standard is CE certification. It needs to undergo strict tensile performance sampling inspection—using a tensile force of 3 times or even higher safety factor until it is broken. There are many types of it, and when using it, you need to consider the shape, thickness, lifting point location, weight and other factors of the precast concrete elements.
Plate spread anchors from HULK Metal feature a welded steel plate and head design, embedded in concrete for edge lifting. Available in various sizes with galvanized options, they support loads up to 10 tons safely.
Unilateral erection anchors serve as specialized lifting inserts for precast concrete, designed for one-sided loading during element erection. They integrate with ring clutches and recess formers, providing stable anchor points that enhance safety and reduce panel stress in construction applications.
HULK Metal supplies flat foot anchors crafted from premium alloys for secure lifting in precast concrete projects worldwide.
HULK Metal stands as a reliable erection anchor supplier in China, delivering high-standard products for precast concrete lifting. Our anchors ensure secure handling with superior strength and corrosion resistance, backed by comprehensive production support for bulk orders.
HULK Metal supplies CE and ISO9001 certified spread anchors with reliable safety factors, faster delivery, and professional support. Choose our spread anchors for superior quality and complete precast lifting solutions.
HULK Metal delivers high-quality two-hole anchors, designed for secure lifting of precast concrete elements. Certified with CE and ISO 9001, our anchors ensure safety, durability, and efficiency.

HULK Metal has been engaged in the production and sales of precast concrete lifting clutch since 2006, and has accumulated rich experience. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a professional team to provide better products and services. Our lifting clutch has passed the CE certification and can pass the destructive test with a 5-fold safety factor. Here you can learn about our product range, production capacity, and service capabilities.
This page presents comprehensive information about precast concrete lifting clutches, including types, structure, materials, production processes, surface treatment options, applications, quality control standards, supplier selection guidance, and factory capabilities.
Ring Clutch supplied by HULK Metal is CE certified and can pass the tensile test with a safety factor of 5. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a complete team to provide better products and services.
HULK Metal's Precast Concrete Lifting Lugs, also known as Lifting Clutches or Lifting Eyes, are precision-engineered for heavy-duty lifting. Manufactured with high-strength materials, they ensure safety, durability, and efficiency in precast concrete lifting applications worldwide.
High-quality dog bone lifting eye with CE and ISO9001 certification. Strong, safe, and durable for precast concrete lifting. Shorter production cycle and faster delivery from trusted Chinese supplier HULK Metal.
HULK Metal supplies CE and ISO 9001 certified lifting clutch for pin anchor with 5 times safety factors, shorter production cycles, and complete after-sales support for global precast concrete projects.
Dog Bone Lifting Eye With Chain supplied by HULK Metal can pass the 5 times safety factor test and has been CE certified. We can provide 1.3 to 20 tons load groups.
Ring Clutch supplied by HULK Metal is CE certified and can pass the tensile test with a safety factor of 5. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a complete team to provide better products and services.
Precast Concrete Lifting Eyes supplied by HULK Metal has passed CE and ISO 9001 Certified and can passed 5 times safety factor testing. HULK Metal is an experienced manufacturer in China. Looking forward your inquire.
Q345/35CrMo/Others
Galvanized/Black/Powder-coat
1.3~32.0
≥5
Precision Casting

HULK Metal offers a wide range of G60, G70, and G80 strength lifting hooks with a well-established supply chain. We have an advanced forging factory and integrated assembly line production. The quality of lifting hooks will be more guaranteed, and we can provide electro-galvanizing, hot-dip galvanizing, and powder coating—three surface treatments. We strictly implement ISO 9001 standard management to provide you with higher quality products and services. You can contact us at any time to visit the factory to understand our production capacity and service capabilities, and then hand over the order to us after you are satisfied.
HULK Metal has a well-established supply chain to provide you with a full range of Clevis Slip Hooks, such as G43, G70, G80, CE marked, with latch or none, electro-galvanized, hot-dip galvanized or powder coated.
We have provided customers in more than 100 countries and regions around the world with Clevis Grab Hooks with strength standards such as G43 70 80 that can pass 2 to 4 Times Safety Factor detection.
HULK Metal is an experienced eye grab hooks supplier in China. We have integrated a complete supply chain and formed a professional team to provide better products and services. We can provide eye grab hooks with various specifications and surface treatments.
HULK Metal is an experienced supplier in China, providing Eye Slip Hooks in various materials, strengths, certifications, surface treatments and sizes. We have established a complete supply chain to ensure that raw materials, production and delivery are under control to provide higher quality and low-cost lifting hooks.

Recess formers are used to place lifting anchors, spread anchors, and other accessories that need to be pre-buried in precast concrete elements. The recess they leave is for the lifting clutch to connect with lifting anchors or spread anchors. We offer a full range of standard recess formers and OEM services for special requirements.
Anchor Recess is an essential component for positioning lifting anchors accurately in precast concrete elements. HULK Metal supplies Anchor Recess in multiple materials and configurations to match different lifting systems and production methods.
HULK Metal provides high-quality Rubber Recess Former for precast concrete lifting systems. They are used with Pin Anchor Recess Former and Spread Anchor Recess Former, ensuring precise recess shaping, shorter production cycles, and faster delivery.
HULK Metal supplies durable lifting pin anchor recess former for precast concrete elements, offering sizes from 1.3 to 32 tons with CE and ISO 9001 certification. Get shorter cycles and comprehensive support for bulk orders.
HULK Metal can provide a variety of precast magnetic formers. With higher quality and a more affordable price, it is your best choice.
The Spread Anchor Rubber Recess Former is made of durable rubber with a reinforced rear metal plate. It is designed for fixing spread anchors in precast concrete, ensuring accurate positioning, easy demolding, and reliable lifting performance.

Precast concrete magnets are one of HULK Metal's main products. They are recognized by customers for their high quality and reasonable price. Precast concrete magnets use high-performance and durable NdFeB alloy magnets. Advanced technology effectively improves production efficiency and reduces costs while ensuring its quality. We provide quality assurance services. You can purchase them with confidence.
As one of the excellent magnetic recess former suppliers in China, HULK Metal has advanced factories and perfect supply chain to provide you with high-quality products and services.
HULK Metal can provide CE-certified magnets for precast lifting and fixing inserts or sockets. Our factory has advanced machining equipment, laser cutting machines, and assembly lines, which can more efficiently complete CE-certified precast lifting fixing insert socket magnet with a higher pass rate.
HULK Metal's Electrical Box Fixed Magnets feature a durable rubber body combined with strong NdFeB magnets, ensuring reliable fixation of electrical boxes in precast concrete. These magnets are customizable in shape, size, and finish, providing flexibility for bulk orders.
Our Shuttering Magnets for Formwork are designed for precast concrete production, offering reusable and stable fixing solutions. They support different mold sizes and deliver better cost-efficiency for large-scale construction projects.
Our Embedded Corrugated Pipe Fixed Magnet combines premium steel housing with powerful magnets to ensure strong fixation during precast concrete production. It reduces installation time, improves efficiency, and provides consistent performance across different applications, helping customers achieve safer and more reliable concrete elements.

HULK Metal also specializes in OEM services for cast-in-channel, T-bolts, wire rope boxes, stone support brackets, and other accessories. Cast in channel can be made of cold-rolled steel, hot-rolled steel, and stainless steel. T bolts are made of carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. Our wire rope box only has one wire rope, and stone support brackets only accept OEM services. We will develop a perfect solution according to your requirements to ensure that the delivery time, quality, and price can meet your requirements.
Steel Embed Plates are essential components used to create strong, reliable connection points within precast concrete structures. As an experienced manufacturer in China, HULK Metal supplies Concrete Embed Plates with stable quality, flexible customization, and consistent production capacity.
Cast In Channel T Bolts from HULK Metal are precision-forged using high-performance alloy steel or stainless steel. Surface treatments, including electro-galvanizing or hot-dip galvanizing, enhance rust resistance, making them reliable for precast concrete connections in construction and infrastructure projects.
HALFEN Anchor Channels from HULK Metal offer superior quality, CE and ISO certified standards, and five times safety factor. Our fast production and delivery, combined with professional after-sales support, make bulk purchasing simple and reliable.
Name Wire Loop Box Precast Concrete Accessories
Molds Full Range Moulds
Materials Wire Rope / Steel Plate / Customized
SL(mm)±10 60 / 80 / 100 / 120 /140
Our Cast in Channel offers superior strength, certified safety, and flexible application for precast construction. Manufactured with advanced processes, it guarantees durability, easier installation, and faster delivery. HULK Metal supports bulk buyers with full technical service and reliable after-sales support.
Our concrete screw bolts are designed for reliable installation without expansion anchors. Galvanized concrete screws provide superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for indoor and outdoor use. HULK Metal offers diverse sizes, surface treatments, and customized solutions to match your needs.
Q345/20#/Stainless steel/Others
Galvanized
0.8~25.0
6~32
≥3
HULK Metal lifting loops are made from alloy or carbon steel, precision-threaded, and electro-galvanized for corrosion resistance. Designed for use with lifting sockets, they ensure safe, reliable handling of precast concrete components with a ≥4 safety factor.
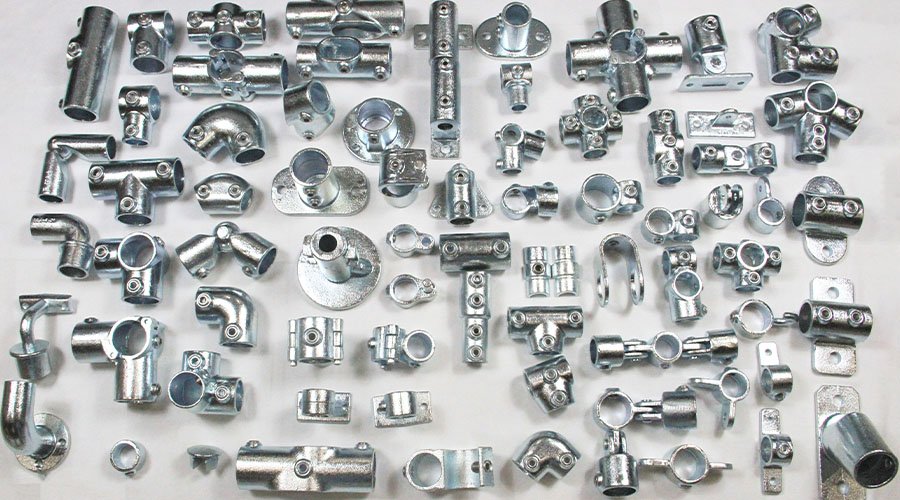

Key clamp fitting can be used with pipe to build many practical structures. We have been engaged in the sales of this series of products since 2006, and now we can provide dozens of fittings with pipe outer diameters such as 1/2", 3/4", 1", 1 1/4", 1 1/2", 2", etc. We have integrated a complete supply chain and a professional team to provide high-quality products and services. You can contact us at any time to get a more suitable price.

Structural pipe fittings are metal parts used to connect pipes of various lengths and diameters using many types of fittings to form a structure with a specific function. It is also often called key clamp fittings or slip-on pipe fittings. Common structures built with it include handrails, guardrails, safety railings, roof guardrails, outdoor amusement facilities, brackets, indoor tables and chairs, etc. HULK Metal can provide structural pipe fittings with pipe diameters of 1/2", 3/4", 1", 1 1/4", 1 1/2", and 2" that are hot dip galvanized, double coated, powder coated, and raw black.
Our handrail bracket structural pipe fittings have multi-type surface treatments to prevent corrosion, precise dimensions, and a strong load-bearing capacity. They provide a longer service life and a more secure installation, making them perfect for outdoor safety rails, balconies, and staircases.
The Internal Swivel Tee Structural Pipe Fitting allows a 360 deg rotation around the connection point, making it ideal for angled rail systems. Manufactured from malleable iron or ductile iron with multiple finish options, it provides stronger performance and longer service life.
The Three Socket Angle Tee Structural Pipe Fitting is an essential component for angled guardrails and handrails. It connects two top rails to an upright post with adjustable angles from 0 to 11 degrees, ensuring both safety and flexibility.
The Slope Short Tee is specially designed for guardrail and handrail systems with slopes from 0 to 11 degrees. Its internal socket allows for the precise adjustment and secure fixing of uprights using hex bolts.
HULK Metal supplies base flange structural pipe fittings made of durable materials with multiple surface finishes. They are designed for stronger pipe connections and longer service life. Our modern factory, professional team, and strict inspection ensure higher-standard products for your projects.
HULK Metal manufactures high-standard railing base flange structural pipe fittings with ISO 9001 certification. Our fittings feature precise dimensions, reliable strength, and multiple surface treatments, ensuring durability and excellent performance in both indoor and outdoor applications for handrail and guardrail systems.
The Short Swivel Tee Structural Pipe Fitting is widely used in handrail and guardrail systems where angled connections are required. Manufactured by HULK Metal with strict ISO 9001 standards, it offers strength, flexibility, and long service life.
Malleable Iron/Ductile Iron/Customizable
Galvanized/Powder-coat/Customizable
TUBE SIZE(mm)
26.9
33.7
42.4
48.3
60.3
33.7/26.9
Customizable
The Swivel Base Flange is engineered to secure pipes to walls with adjustable angles from 0° to 180°. Its modular design ensures easy assembly, reliable stability, and compatibility with multiple pipe sizes and materials.
The Corner Swivel Combination structural pipe fitting is designed to connect pipes set at right angles across perpendicular planes.
The Add on Crossover, also known as Split Crossover, is designed for adding a perpendicular pipe to an already installed system. Its split-sleeve structure makes installation easy without dismantling existing pipes.
The 90 Degree Two Way Elbow structural pipe fitting is designed for connecting two pipe ends at a right angle. It is commonly applied in handrail, guardrail, and fence systems, ensuring strong and stable joints.
Our Four Socket Cross Structural Pipe Fitting comes in various sizes and surface treatments to suit different projects. Made from malleable iron or ductile iron and customizable on request, these fittings are durable and corrosion-resistant.
Clamp on Crossover Structural Pipe Fittings are designed to create perpendicular connections between pipes without requiring dismantling of existing structures. They feature a strong clamping design that ensures tight, gap-free joints.
The Offset Crossover Structural Pipe Fitting is designed to connect two pipes securely in an offset crossing structure. It allows builders to easily create strong and stable frameworks while maintaining flexibility for different structural needs.
The 90 Degree Two Socket Tee offers two perpendicular sockets for secure pipe connections. It is engineered to provide precise alignment and exceptional strength in guardrails, handrails, fencing, and DIY structures.
Three Socket Cross Structural Pipe Fittings connect vertical uprights with three perpendicular horizontal pipes, offering robust support for fencing, storage racks, and DIY systems. Their versatile design allows easy installation and configuration, ensuring durability and stability in multiple applications.
HULK Metal's Clamp on Tee Structural Pipe Fittings are engineered for secure, easy installation on existing systems. Made from high-quality malleable or ductile iron, they support durable, stable connections for guardrails, handrails, and DIY structures.
Two Socket Cross Structural Pipe Fittings are designed to connect upright pipes with two perpendicular pipes in the same plane. Manufactured from high-quality cast iron, stainless steel, or aluminum, these fittings undergo strict inspection and advanced surface treatment
Malleable Iron/Ductile Iron/Customizable
Galvanized/Powder-coat/Customizable
TUBE SIZE(mm)
26.9
33.7
42.4
48.3
Customizable
HULK Metal manufactures high-quality Three Socket Tee (Long Tee) Structural Pipe Fittings that combine strength, precision, and reliability. Made from malleable or ductile iron with customizable finishes such as galvanizing or powder coating, these fittings are ideal for both industrial and DIY applications.
The side outlet elbow, also called a 3-way elbow, is designed to connect three pipes at 90° angles. It provides strength and stability in guardrails, handrails, and cube-like structures.
HULK Metal's Variable Swivel Elbow is engineered for versatile pipe-joining applications. With angles ranging from 73° to 287°, it provides maximum flexibility for complex structures.
HULK Metal's Reducing Short Tee Structural Pipe Fitting is engineered to provide a secure vertical pipe connection with different diameters, ideal for mid-rails or guardrail top rails.
The Single Socket Tee Structural Pipe Fitting, also known as Short Tee, is widely used in railing systems, guardrails, and DIY structures. It allows one pipe to connect securely at a right angle to another, forming a stable "T" connection.
The Single Lugged Bracket Structural Pipe Fitting is a reliable solution for fixing pipes onto walls or panels where limited space prevents double lug use.
The Vertical Railing Side Support Structural Pipe Fitting is designed to provide strong and stable support for railing systems. Manufactured with malleable iron or ductile iron, and available in multiple surface treatments such as hot-dip galvanizing or powder coating, these fittings ensure long-term durability.
The Cradle Clamp Structural Pipe Fitting is designed to fasten pipe rails securely to uprights. Its open clamp structure allows quick installation, while inner hex bolts ensure reliable stability.
Horizontal Railing Side Support Structural Pipe Fittings are designed to fasten railing uprights firmly against walls or side structures.
The Adjustable Short Tee is engineered to connect pipes at variable angles from 30 deg to 60 deg. Its durable structure, simple installation, and flexible design make it suitable for guardrail and handrail systems.
The Single Swivel Combination is formed by joining two swivel fittings, making it ideal for environments requiring flexible angle adjustments. While it cannot independently bear lateral loads, it becomes effective when used together with other fittings.
The Add on Short Tee Structural Pipe Fitting is a hinged socket fitting that allows vertical connections to existing pipe systems without dismantling.
HULK Metal Variable Elbow Structural Pipe Fitting is designed to create secure and adjustable angled connections between pipes. With a strong structure and reliable locking bolts, it delivers stability and precision.
HULK Metal Adjustable Angle Two Socket Cross Structural Pipe Fitting provides a strong and flexible connection between uprights and rails. Designed for rail systems with slopes from 45° to 90°, it is widely used in stairways, handrails, and ramps.
The Galv Ground Socket Structural Pipe Fitting is designed to provide secure support for uprights in diverse ground conditions. Made of high-strength malleable or ductile iron, it ensures long-term stability and durability.
The Side Palm Fixing Structural Pipe Fitting is engineered to provide a solid and secure connection for railing uprights against walls, stairs, or ramps. Its three-lug design with reinforced sockets improves stability and load capacity.
The Double Lugged Bracket Structural Pipe Fitting is engineered to mount pipes flush against flat walls or panels. Featuring two lugs with fixing holes, it supports various screw or chemical fixing methods. Its socket with hex bolts firmly secures the pipe in place.
The Double Male Swivel Structural Pipe Fitting is designed for flexible joint connections and works seamlessly with single swivel female parts to form a stable structure.
Malleable Iron/Ductile Iron/Customizable
Galvanized/Powder-coat/Customizable
TUBE SIZE(mm)
26.9
33.7
42.4
48.3
60.3
Customizable
Hook structural pipe fittings provide temporary mounting points on pipes. Designed for horizontal and vertical installation, they ensure user safety with rounded heads and secure locking via hex bolts. This solution is suitable only for incomplete systems.
The slope railing base flange pipe fitting is designed to secure inclined uprights to the ground with adjustable angles. Manufactured with strict quality control, it offers multiple surface treatments, ensuring strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for diverse railing and structural applications.
Our gate hinge pipe fittings combine robust materials with precision casting to create dependable connections for gates. With multiple surface treatments and sizes available, they meet diverse installation requirements, deliver excellent corrosion resistance, and provide a secure, smooth rotational function.
Gate Eye Pipe Fittings provide a reliable hinge connection for gates and handrail systems. Made from strong cast iron or flexible ductile iron, they come with different surface finishes, providing great performance, a longer lifespan, and making them suitable for many construction and industrial uses.

Galvanized pipe handrail fittings are slip-on pipe fittings that connect pipes through sockets and use side grub screws to fasten the entire handrail. Its surface treatment includes hot-dip galvanizing and double-layer galvanizing. The latter is more expensive but the coating is thicker and more beautiful. HULK Metal has a complete supply chain and a professional team to provide a full range of products and services. You can download our product catalog or directly inquire.
No. 101 galvanized pipe handrail fittings are used to connect two pipes into a "T" shape. It is also called a Pipe Clamp Short Tee. One pipe is inserted into the socket, and the other one passes through the channel above.
101 Reducing Short Tee Galvanized Pipe Railing Fittings are often used. HULK Metal is a well-known supplier in China. We look forward to your inquiry.
104 galvanized slip-on pipe fittings long tee can be used to add two horizontal pipes to the guardrail or handrail uprights, or to connect two pipes in a DIY structure and add a vertical pipe to them.
104 galvanized slip-on pipe fittings long tee can be used to add two horizontal pipes to the guardrail or handrail uprights, or to connect two pipes in a DIY structure and add a vertical pipe to them.
116A Galvanized Pipe Guardrail Fittings Add On Side-outlet Tee is used to add two perpendicular rails to an already assembled handrail or guardrail uprights, or to add two perpendicular pipes to an assembled DIY structure such as a cube or cuboid.
119 Galvanized Safety Railing Fittings Two Socket Cross is used to add two pipes on the same plane to form a cross structure for a specific position of a pipe.
We integrated a complete supply chain, passed ISO 9001 certification, formed a professional technical team and produced a full range models of the galvanized pipe connector fittings to provide the best services and products. Looking forward your inquiry.
The 119A Galvanized Railing Connectors Add-on Two Socket Cross is different from the 119 type in that it can add two pipes to an already completed system.
123 Galvanized Railing Fittings 40 to 70 Elbow is very easy to use and can be used in any scenario where two pipes need to be connected at an angle of 40 degree to 70 degree. We have a complete supply chain and provide QA services.
124 type Galvanized Key Clamp Fitting uses 3 types of hot-dip galvanizing, double coating, and powder coating. We can provide 33.7mm, 42.4mm and 48.3mm diameters. We integrate a complete supply chain and a professional team to provide better products and services. Looking forward to your inquiry.
We can provide 21.3 mm to 60.3 mm size, that is, 1/2" to 2". We have a full range of molds, can complete each order faster.
Safety rail fittings are slip-on pipe fittings for safety railings. They can be quickly installed to complete a system, are easy to operate, and have a longer life and better performance. The 125R reducing 90-degree elbow is a special and uncommon fitting used to connect two pipes of different thicknesses.
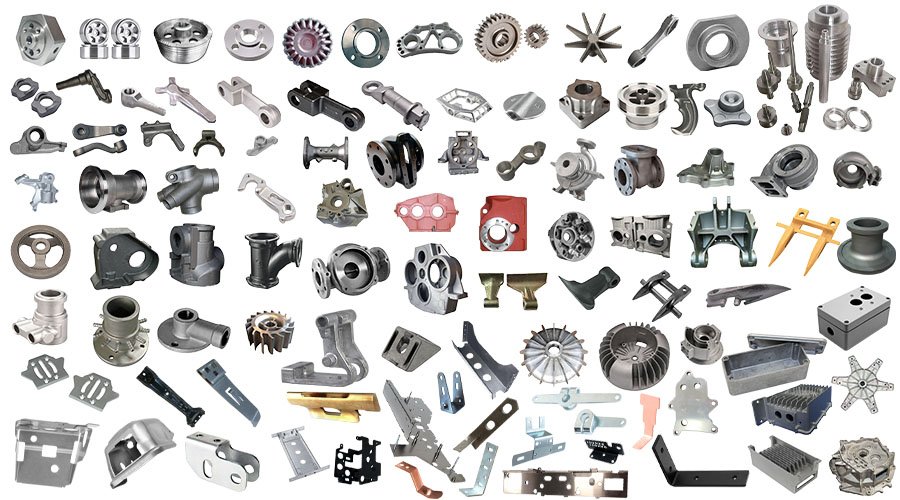

Custom metal parts are non-standard components with special shapes, tolerances, and functions, designed for use in various industries such as automotive manufacturing, construction, machinery production, and decoration. They are made from raw materials like steel, iron, aluminum, and copper through processes such as casting, forging, CNC machining, and sheet metal fabrication. HULK Metal has been providing custom metal parts OEM services to customers around the world since 2004. We have now formed a professional team that can design solutions based on your drawings to save more costs and ensure the quality of the goods. We provide QA services and look forward to your consultation.

Casting spare parts are metal workpieces with special shapes, sizes, and functions made from various metals using appropriate metal casting processes. HULK Metal integrates a complete metal foundry to complete casting spare parts that require sand casting, investment casting, lost foam casting, or die casting. Currently we can process metal parts made of ductile iron, gray iron, malleable cast iron, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum, etc. We have passed ISO9001 certification. The experienced technical team can develop a more complete solution based on your drawings and calculate a more competitive quotation. We provide QA services. Looking forward to your inquiry.
Aluminum Die Casting Parts are widely used for structural and functional components requiring strength, accuracy, and clean surfaces.
Sand Casting Parts are widely used for producing durable metal components with complex shapes and stable performance. As an experienced Sand Casting Parts manufacturer, HULK Metal provides Custom Sand Casting Parts and OEM Sand Casting Parts based strictly on customer drawings.
Name Aluminum Die Casting TV Brackets
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting Seat Brackets
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting Pump Covers
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting PC Bracket
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting Motorcycle Accessories
Manufacturing According to Drawings
CNC Machining Turning, Milling, Planing, Drilling, Grinding, Drilling, Boring
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting Motor Fan
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting LED Light Heat Sink
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting LED Light Cover
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
A Die Casting Junction Box made from aluminum offers reliable protection, precise structure, and stable performance for electrical systems.
HULK Metal offers premium Aluminum Die Casting Heatsinks through a fully integrated OEM process, including die casting, CNC machining, surface treatment, and quality inspection.
Name Aluminum Die Casting Connectors
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting Bicycle Accessories
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Steel Casting Parts are widely used for load-bearing and structural components requiring strength, durability, and dimensional stability.
Name Aluminum Die Casting Auto Accessories
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Name Aluminum Die Casting Accessories
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Aluminum Alloy 6063 / Customized
Profile Extrusion / Cutting / Deburring / CNC Process / Customized
Air conditioner / Frequency Converter / Communication Base Station / Computer / Electric Equipment / Customized
CE / ISO / RoHS / SGS / Customized
Anodizing / Sand Blasting / Painting / Chormating / Customized
Trademark printing / wooden box / plastic box / foam box / air film / Customized
Die Cast Aluminum Enclosures are widely used to protect electronic and industrial components in demanding environments.
We manufacture bike parts strictly according to customer drawings, covering drivetrain, braking, wheel, and structural components. Our OEM service integrates casting, CNC machining, surface treatment, packaging, and logistics under one managed process.
Name Aluminum Die Casting Washing Machine Bracket
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
HULK Metal provides OEM Precision Die Casting Parts with full technical support, strict quality control, and reliable production.
HULK Metal delivers high-quality OEM casting aluminum brackets made to your exact drawings, using die casting, sand casting, or investment casting.
HULK Metal provides comprehensive Aluminium Die Casting Auto Parts solutions, covering engine, transmission, chassis, and electronic components. We meticulously manage every stage, from mold design, die casting, CNC machining, and surface treatment, to strict quality control, packaging, and delivery.
HULK Metal has provided excellent Agricultural Machinery Casting services to hundreds of customers worldwide.
HULK Metal supplies Automobile Casting Components for global automotive manufacturers and bulk buyers seeking reliable OEM partners in China. With ISO 9001 certified factories and mature casting experience, we produce Automobile Casting Parts strictly according to drawings.
HULK Metal specializes in OEM/ODM casting of Custom Flail Mower Hammer Blades. With an ISO 9001-certified factory, advanced foundry capabilities, and end-to-end quality control, we deliver wear-resistant, dimensionally accurate blades tailored to your machinery.
Aluminum Alloy 6063 / Customized
Profile Extrusion / Cutting / Deburring / CNC Process / Customized
Air conditioner / Frequency Converter / Communication Base Station / Computer / Electric Equipment / Customized
CE / ISO / RoHS / SGS / Customized
Anodizing / Sand Blasting / Painting / Chormating / Customized
Trademark printing / wooden box / plastic box / foam box / air film / Customized
Die Casting Engine Parts are widely used in automotive and industrial power systems where strength, accuracy, and heat dissipation matter.
HULK Metal is a trusted manufacturer of Custom Sickle Guards Casting, serving bulk buyers worldwide. Our ISO 9001-certified foundry delivers high-precision sickle guards in ductile iron, grey iron, or cast steel—tailored to your drawings.
HULK Metal delivers precise and durable Water Glass Sand Casting components for industrial and OEM applications. Combining advanced factories, CNC machining, comprehensive surface treatments, and rigorous quality control, we ensure reliable production and timely delivery.
Our Stainless Steel Castings are produced for demanding industrial applications where strength, corrosion resistance, and consistency matter. As an OEM-focused supplier, we manufacture strictly according to your drawings using sand casting, investment casting, or lost foam casting.
Resin sand casting is widely used for medium and large metal parts requiring good surface finish and stable structure.
HULK Metal provides professional reducer housing casting services, offering horizontal, vertical, integral, and split designs. Our complete OEM solutions include casting, CNC machining, surface treatment, quality inspection, packaging, and global delivery.
Name Precision Casting Castings
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Cast Iron / Aluminum / Stainless Steel / Carbon Steel / Gray Iron / Customized
Process Investment Casting / Ceramic Mold Casting / Metal Mold Casting, Die Casting, Lost Foam Casting
Surface Treatment Sandblasting / Shot Blasting / Powder Coating / Customized
Test Content & Data 1. Chemical composition; 2. Mechanical properties; 3. Metallographic inspection; 4. Inspection of appearance, size, shape, and position tolerance; 5. Surface roughness;
HULK Metal operates as a trusted Casting Motorcycle Parts manufacturer in China, specializing in aluminum die casting and sand casting motorcycle parts. Backed by ISO 9001 standards, our factories deliver precision OEM components tailored to your drawings.
Lost wax casting is ideal for producing complex metal parts with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances. As an experienced lost wax casting foundry in China, HULK Metal provides reliable OEM services based on your drawings.
HULK Metal provides comprehensive lost foam casting solutions for OEM projects, covering mold design, casting, CNC machining, surface treatment, and quality inspection.
Investment casting produces complex metal parts with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances through a precise lost wax process.
HULK Metal delivers ISO 9001-certified grey iron casting services with precision, durability, and cost efficiency.
HULK Metal has provided excellent metal casting services to hundreds of ductile iron casting parts purchasers around the world. More than 20 industries, including automobile manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, home appliance manufacturing, construction, agriculture, and energy, have used our products.
HULK Metal delivers high-quality custom cast iron drain pipe fittings through ISO 9001-certified factories. Our experienced team ensures precise production from drawings, rigorous quality control, and timely delivery.
You will get higher quality Centrifugal Casting Castings. HULK Metal has an advanced centrifugal casting production line that can produce cast iron, gray iron, ductile iron, stainless steel, high manganese steel and other raw materials.
HULK Metal has provided excellent metal casting services to hundreds of Cast Iron Casting parts purchasers around the world. Our products have been used in more than 20 industries, such as automobile manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, home appliance manufacturing, construction industry, etc.

There are many forging parts suppliers in the world, and their company sizes vary, with different production capabilities and services. HULK Metal is one of the well-known forging parts suppliers in China. We have been providing forging parts production and export services to global customers since 2004 and have rich experience. We have a complete supply chain and service team to provide more thoughtful services, help solve more problems that arise during order production, and protect your rights and interests by providing after-sales service.
Precision forging is a near-net-shape manufacturing process that creates high-strength components with superior mechanical properties. At HULK Metal, our OEM services integrate advanced hot and cold die forging with precision CNC machining.
HULK Metal provides a comprehensive OEM solution for high-precision forged steel parts, integrating advanced hot and cold forging factories with elite 5-axis CNC machining.
Description HULK Metal provides a vertically integrated manufacturing solution for Motorcycle Forged Parts, specializing in high-strength components like crankshafts, connecting rods, and triple clamps.
Mining environments demand components with exceptional wear resistance. HULK Metal manufactures custom mining forged parts using premium carbon and alloy steels.
ISO 9001-certified metal forging factory. The technical team supports every phase—from print review to process optimization. Faster turnaround without sacrificing accuracy. Full QA with returns/rework guarantee.
Forged gear blanks provide higher strength, better grain flow, and improved fatigue resistance compared with cut gears.
Forging small parts are widely used where strength, consistency, and tight tolerances matter. HULK Metal provides OEM services for custom forging small parts based on drawings or samples.
HULK Metal provides premium forged flanges manufactured with hot die forging and precise CNC machining. Our services cover raw material selection, surface treatment, strict quality inspection, and timely delivery.
Custom forged parts from HULK Metal offer superior strength, reliability, and performance across industries like automotive, construction, and energy. Using advanced forging techniques and a comprehensive quality control system, we provide parts made to your exact specifications.
Closed die forged parts are produced by shaping heated metal within precision dies, delivering higher strength, consistent grain flow, and tight tolerances.
HULK Metal’s forged components include manufacturing processes, materials, surface treatments, and quality control measures. From automotive to industrial applications, our forged components deliver superior performance and reliability
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Process Casting / Forging / Stamping
CNC Machining Turning, Milling, Planing, Drilling, Grinding, Drilling, Boring
Materials 304 / 316L / Aluminum Alloy / Customized
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Process Casting / Forging / Stamping
CNC Machining Turning, Milling, Planing, Drilling, Grinding, Drilling, Boring
Materials Carbon Steel / ND Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum Alloy / Customized
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Process Casting / Hot Forging
CNC Machining Turning, Milling, Planing, Drilling, Grinding, Drilling, Boring
Materials Carbon Steel / ND Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum Alloy / Customized
HULK Metal specialises in high-quality forged stainless steel parts and offers comprehensive OEM services. As a certified ISO 9001 factory in China, we ensure strict quality control, competitive pricing, and rapid order turnaround.
Name Motorcycle Parts Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum / Customized
Process Hot Forging / Cold Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Rilling Forging / Die Forging / Customized
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Process Hot Forging / Die Forging / Custom
CNC Machining Turning, Milling, Planing, Drilling, Grinding, Drilling, Boring
Materials Carbon Steel / ND Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum Alloy / Customized
Name Motorcycle Accessories Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum / Customized
Process Hot Forging / Cold Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Rilling Forging / Die Forging / Customized
Name Mining Machinery Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel / Customized
Process Hot Forging / Cold Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Die Forging / Customized
Custom hot forging parts are produced through controlled heating, precision die forging, machining, inspection, and delivery. HULK Metal supports OEM projects based on drawings, combining experienced technical teams, coordinated factories, and ISO 9001 management.
Name Cold Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials 20Cr Steel / 20CrMo Steel / 20CrMnTi Steel /Aluminum / Aluminum Alloy / Customized
Process Cold Forging
Carbon Steel Forged Parts are widely used in applications where strength, durability, and dimensional stability are important. HULK Metal supplies Custom Carbon Steel Forged Parts through full OEM services, from drawing review, forging, machining, surface treatment to delivery.
Name Bicycle Accessories Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum / Customized
Process Hot Forging / Cold Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Rilling Forging / Die Forging / Customized
Name Auto Parts Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum / Customized
Process Hot Forging / Cold Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Rilling Forging / Die Forging / Customized
Name Auto Accessories Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel / Aluminum / Customized
Process Hot Forging / Cold Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Rilling Forging / Die Forging / Customized
Name Alloy Steel Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Alloy Steel
Process Hot Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Rilling Forging / Die Forging / Customized
Name Agricultural Machinery Accessories Forging Parts
Manufacturing Methods Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel / Customized
Process Hot Forging / Free Forging / Mold Forging / CNC Machining / Customized

Metal stamping parts are metal components with special shapes, sizes and functions that are made of metal sheets by blanking, deep drawing, bending, punching and other processes. Common metal sheets are made of galvanized iron, galvanized steel, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc. HULK Metal is a Chinese supplier with an advanced sheet metal manufacturing plant. We can provide you with OEM and ODM services such as cutting, welding and stamping. We will sign an NDA agreement with you and provide after-sales service. You can rest assured to place your order with us.
HULK Metal is a manufacturer of sheet metal stamping parts in China. We have advanced stamping equipment, experienced workers, and perfect after-sales service to complete higher-quality orders faster at a lower price.
HULK Metal is committed to providing high-quality sheet metal automotive parts OEM services to customers around the world. We have a complete supply chain to provide you with better OEM services.
HULK Metal has developed over 16 years to become an experienced metal stamping manufacturer. We can manufacture higher quality steel metal stamping parts from carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. We have a complete quality control system.
HULK Metal has provided excellent metal stamping services to hundreds of stainless steel metal stamping parts purchasers around the world. Our products have been used in more than 20 industries, such as automobile manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, home appliance manufacturing, construction industry, etc.
HULK Metal is a professional manufacturer of home appliance metal stamping parts that has provided metal stamping services for the home appliance manufacturing industry for over 16 years.
Aluminum Alloy 6063 / Customized
Profile Extrusion / Cutting / Deburring / CNC Process / Customized
Air conditioner / Frequency Converter / Communication Base Station / Computer / Electric Equipment / Customized
CE / ISO / RoHS / SGS / Customized
Anodizing / Sand Blasting / Painting / Chormating / Customized
Trademark printing / wooden box / plastic box / foam box / air film / Customized
As a metal stamping service supplier with a strong production capacity, HULK Metal has 5 sets of stamping machines with a capacity of 315 tons, 5 sets of 200 tons capacity, 5 sets of 80 tons capacity and 5 sets of 60 tons capacity. We can provide customized manufacturing services for copper metal stamping parts of 0.1mm~10mm. Products can be certified by CE, SGS, GB, and other standards.
HULK Metal has 20 precision stamping machines that can process precision metal stamping parts from 0.05mm to 5mm. Our quality inspection team will strictly test the performance and parameters of the product to ensure that the quality of the product can meet your requirements.
HULK Metal has provided excellent metal stamping services for more than 20 industries such as automobiles, home appliances, machinery, and other manufacturing or construction industries.
HULK Metal has an experienced technical team that can customize complete custom stamping parts OEM solutions. We can supply products certified by CE, SGS, etc. and comprehensive services such as shipping and after-sales. You can buy metal stamping parts you want more easily at HULK Metal.
HULK Metal provides Custom Construction Metal Stamping Services for bulk buyers who demand precision, strength, and consistency.
HULK Metal is a professional manufacturer of metal stamping parts. Our factory has more automated stamping machines and advanced product quality inspection instruments so that we can complete higher quality carbon steel metal stamping parts faster.
HULK Metal provides professional brass metal stamping services with full-process technical support and production capacity. We specialize in manufacturing custom brass metal stamping parts that meet CE, GB, and SGS standards.
HULK Metal's factory has 20 stamping machines, 10 CNC machines, and perfect-quality inspection instruments. We can provide complete OEM services for metal stamping parts. We can manufacture metal stamping parts in automobiles, construction, household appliances, and other industries with copper, steel, and aluminum as raw materials.
HULK Metal is a professional Auto Accessories Metal Stamping Parts manufacturer with over 16 years of experience. We have a complete supply chain to supply you with complete metal stamping OEM services.
HULK Metal has been engaged in the manufacture of Aluminum Sheet Metal Stamping Parts for many years. We focus more on the needs of our customers and develop complete production solutions accordingly.
HULK Metal has been engaged in the stamping service of aluminum metal parts since the second half of the 20th century. Up to now, HULK Metal has been able to produce metal stamping parts with a thickness of 0.1mm~2mm using 1000~7000 aluminum alloy plates as raw materials.

Machined metal parts are components with more precision and special functions that are made by CNC machining centers using turning, milling, grinding, drilling, and other tools to process metal billets or semi-finished castings and forgings. They are widely used in the automotive, construction, and machinery industries and various other industries. HULK Metal is a China-machined metal parts supplier that can provide OEM and ODM services and make more perfect solutions according to your drawings and requirements to ensure faster delivery of goods with higher quality and better prices. We provide after-sales service; please rest assured to purchase.
HULK Metal provides high-precision CNC machining services for parts made from steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and alloys.
HULK Metal provides high-quality Aluminum CNC Machining Parts, combining advanced multi-axis CNC machining, precise surface treatments, and strict quality control.
Aluminum Alloy 6063 / Customized
Profile Extrusion / Cutting / Deburring / CNC Process / Customized
Air conditioner / Frequency Converter / Communication Base Station / Computer / Electric Equipment / Customized
CE / ISO / RoHS / SGS / Customized
Anodizing / Sand Blasting / Painting / Chormating / Customized
Trademark printing / wooden box / plastic box / foam box / air film / Customized
HULK Metal delivers high-precision CNC auto parts through ISO 9001-certified factories in China, offering full OEM machining services—from design review and material sourcing to surface treatment, rigorous inspection, and global delivery.
Name CNC Machining Aluminum Die Casting Parts
Manufacturing According to Drawings
Materials Al-Mg Alloy / Al-Zn Alloy / Al-Si Alloy / Customized
Surface Anodized / Passivated / Polished / Powder Coating / Brushed / Customized
Precision Machining for Agricultural Parts requires stable accuracy, durable materials, and consistent production control. HULK Metal provides Agricultural Sector Parts Machining Services based on customer drawings, covering turning, milling, drilling, and finishing.
Precision bicycle part machining demands tight tolerances, lightweight strength, and flawless surface finishes—exactly what HULK Metal delivers.
HULK Metal delivers precision custom flange machining based on your drawings, using advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC equipment in ISO 9001-certified factories.

Pump parts are the components that make up the pump, including the body, housing, cover, impellers, brackets, etc. Valve parts are composed of the body, handle, stem, gate (gate valve), disc (butterfly valve), ball (ball valve), etc. These metal parts are made of ductile iron, gray iron, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy through casting, forging, CNC processing, and other processes. HULK Metal has passed ISO 9001 certification and has been providing OEM and ODM services for pump and valve parts since 2004. Looking forward to your inquiry.
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Sewage Pump Impellers
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron pump impellers: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel pump impellers: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Sewage Pump Housing
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron Sewage Pump Housing: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel Sewage Pump Housing: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Sewage Pump Bases
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron Sewage Pump Bases: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel Sewage Pump Bases: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Pipeline pump Motor Bracket
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron Pipeline pump Motor Bracket: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel Pipeline pump Motor Bracket: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Pipeline Pump Impellers
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron Pipeline Pump Impellers: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel Pipeline Pump Impellers: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Pipeline Pump Covers
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron Pipeline Pump Covers: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel Pipeline Pump Covers: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Pipeline Pump Housings
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron Pipeline Pump Housings: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel Pipeline Pump Housings: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Centrifugal Pump Impellers
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron pump impellers: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel pump impellers: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
1. Chemical composition; 2. Mechanical properties; 3. Metallographic inspection; 4. Inspection of appearance, size, shape, and position tolerance; 5. Surface roughness;
Centrifugal Pump Covers
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron pump covers 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel pump covers: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Name Centrifugal Pump Bottom Plates
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron Centrifugal Pump Bottom Plates: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel Centrifugal Pump Bottom Plates: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Powder spraying, Painting
Manufacturing According to Drawings
QT (Ductile Iron) HT (Grey Cast Iron) Cast Steel (ZG25)
Gray cast iron, ductile iron pump Housings: 1. Resin sand casting; 2. Lost foam casting; 3. Coated sand casting;
Cast steel pump Housings: precision casting, lost wax casting.
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized
Ductile Iron / Stainless Steel / Gray Iron / Cast Steel / Customized
+/-0.01mm
CT9
Casting / CNC / Customized
≥1.6Mpa, ≤6.4Mpa
Painting / Plating / Polishing / Customized
Anti-collision / Brand Logo / Customized
CB / CE / URV / Customized

HULK Metal delivers high-precision gym equipment parts engineered for commercial durability and performance. Leveraging advanced manufacturing processes—including casting, forging, stamping, and welding—we produce components that meet tighter tolerances, higher load capacities, and longer service life compared to conventional alternatives. Every part is crafted from premium materials like steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, and undergoes rigorous quality checks. Our customization capabilities allow seamless integration into any commercial custom gym equipment system, ensuring reliability, consistency, and scalability for global fitness brands seeking a trusted OEM partner.
HULK Metal provides premium push sleds designed for professional training and commercial gyms, offering diverse types, robust construction, and customizable features.
This product detail focuses on Monolift Rack Attachments. It covers features, manufacturing processes, quality control, and benefits.
HULK Metal provides premium OEM squat racks, including power racks, half racks, wall-mounted, foldable, and combo designs. Each rack is produced with precision metalworking, strict quality inspections, and advanced surface treatments.
HULK Metal''s Safety Spotter Arms are engineered for strength, safety, and long-term durability in commercial and home gym racks. Manufactured with high-quality steel, precise welding, and advanced surface treatments, each unit undergoes strict inspection and testing.
HULK Metal provides a comprehensive OEM manufacturing solution for rear base stabilizers, focusing on structural integrity and precision. Utilizing advanced robotic welding, CNC laser cutting, and professional surface treatments, we ensure every component achieves a 99.8% precision rate.
HULK Metal provides a comprehensive OEM manufacturing solution for high-strength fitness crossmembers, serving as the structural backbone for commercial power racks and functional rigs. By integrating ISO 9001-certified processes with advanced CNC laser cutting and robotic welding, we deliver rack crossmember components with a 99.8% precision rate.
HULK Metal provides durable, safe, and customizable medicine ball holder racks, including vertical, horizontal, and modular designs. With integrated factory resources, strict quality control, certified production, and comprehensive OEM services, we ensure faster delivery, competitive pricing, and reliable after-sales support. Ideal for commercial gyms, training centers, and bulk buyers seeking high-quality, long-lasting fitness storage solutions.
HULK Metal provides a comprehensive OEM solution for high-quality front foot extensions, utilizing advanced robotic welding, laser cutting, and ISO 9001-certified quality control. We deliver precision-engineered stabilizers that enhance equipment safety and footprint integrity for global fitness brands. Our vertically integrated factory ensures competitive pricing, rapid production cycles, and a 99.8% precision rate. Backed by a lifetime quality guarantee, we empower procurement teams to streamline their supply chain with durable, high-performance metal components.
HULK Metal provides a comprehensive OEM manufacturing solution for high-capacity dumbbell stands, prioritizing structural integrity and long-term durability. Our facility integrates ISO 9001 standards with advanced robotic welding and CNC laser cutting to achieve a 99.8% precision rate. From heavy-duty tiered racks to space-saving vertical towers, we manage the entire lifecycle—from raw material inspection to global logistics—delivering cost-effective, commercial-grade storage solutions that meet the rigorous safety and aesthetic demands of professional fitness environments.
HULK Metal provides a comprehensive OEM solution for the dip bar attachment, integrating high-wattage laser cutting and robotic welding to achieve a 99.8% precision rate. Our facility specializes in heavy-duty structural steel fabrication, offering diverse surface treatments like electrostatic powder coating for maximum durability. By optimizing our vertically integrated supply chain, we deliver certified, commercial-grade dip attachment units at competitive prices with accelerated lead times, ensuring a stable and high-quality inventory for global fitness brands.
HULK Metal provides high-capacity OEM manufacturing for commercial-grade Chin Up Bars, utilizing over 50 automated welding stations and high-speed fiber laser cutting. Our ISO 9001-certified factory ensures every component meets a 99.8% precision rate, delivering structural safety and aesthetic consistency.
Our heavy-duty Barbell Holder Attachment is engineered for seamless integration into commercial power racks and home gym systems. Utilizing high-grade steel and precision laser cutting, we provide comprehensive OEM services that transform your technical drawings into market-ready components.
HULK Metal delivers industrial-grade Weight Plate Tree manufacturing, transforming complex technical drawings into durable gym hardware. Our Bar and Weight Plate Tree OEM services prioritize structural integrity through advanced metalworking.
Our J Hooks and J Cups for Power Rack OEM services are designed for brands and wholesalers sourcing in volume. HULK Metal supports full-process manufacturing from drawings, covering stamping, welding, machining, and surface treatment under ISO 9001 control.
Fitness Equipment Extrusions are widely used for frames, rails, supports, and structural connectors in commercial gym equipment. HULK Metal provides OEM production covering extrusion forming, precision cutting, CNC machining, welding, and surface treatment.
HULK Metal provides Weight Plate Holder OEM services for global gym equipment brands and wholesalers seeking dependable large scale supply. From standard weight plate racks to custom bumper plate storage solutions, our factories support cutting, welding, bending, machining, and finishing under ISO 9001 systems.
Fitness Equipment Parts often involve complex structures, load-bearing requirements, and strict consistency standards. HULK Metal provides Custom Fitness Equipment Parts through OEM production, supporting drawings or samples.
Exercise equipment parts form the structural and functional backbone of modern fitness machines. HULK Metal offers OEM services focused on custom exercise equipment parts manufactured strictly to drawings.
HULK Metal crafts Custom Workout Equipment Parts to your exact drawings—no job too complex. With full in-house metal fabrication and strict ISO controls, we deliver stronger, smoother, and more consistent parts than typical suppliers.
HULK Metal Crafts Gym Equipment Components with tighter tolerances and heavier-duty builds than most. We handle OEM requests from start to finish—stamping, welding, laser cutting, and forging—all under one roof.
HULK Metal delivers high-quality custom barbell rack OEM services backed by decades of metal fabrication expertise. Our ISO 9001-certified factories handle everything from raw material sourcing to final delivery. Whether you need power racks, squat racks, or wall-mounted systems, we produce precise, durable parts that meet your exact specifications.
HULK Metal is a trusted OEM supplier of custom gym equipment rack and parts, backed by ISO 9001-certified factories and full-sheet metal production capabilities. We manufacture power racks, squat racks, wall-mounted systems, and more—exactly to your drawings.
HULK Metal produces custom power racks from iron, steel, stainless steel, and aluminum using sheet metal, profiles, pipes, and strips. Our processes include stamping, CNC machining, welding, casting, and forging.

When a wire rope or cable needs to be pulled or tightened, a fulcrum is often needed. This requires a tool that can be used to hold the wire rope or cable firmly and provide a loop for hanging the hook. The wire rope cable puller Gripper was born under this circumstance. It has many styles: the first one is made by intertwining metal mesh, which can clamp the cable and provide a connection point after being tightened on one end of the cable. The second one clamps the cable through a jaw at one end, and the loop at the other end can connect the hook and the lock.

HULK Metal's Jaw Wire Cable Puller Grippers are designed to provide strong grip, smooth pulling, and enhanced safety in cable tensioning applications. Built with high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques, our pullers deliver consistent performance under demanding conditions. Whether you need sawtooth-type or round-type models, our range meets various load capacities and cable sizes. Backed by strict quality control and comprehensive production capabilities, we ensure each gripper meets international standards. With OEM services available, we help customers worldwide get customized solutions that fit their exact cable pulling needs.
HULK Metal offers durable come along clamps engineered for high performance in overhead line construction and industrial cable installation. Each clamp provides a strong, slip-resistant grip on conductors, ensuring safe tensioning and pulling.
HULK Metal provides a wide range of wire grips designed for copper cables, aluminum conductors, guy wires, and steel ropes. Our Wire Pulling Grips are precision-forged, durable, and tested to handle demanding loads without damaging conductors.
As a Chinese manufacturer of heavy-duty Wire Rope Puller Tools, we hope to provide high-quality products to more customers around the world. To this end, we will pay more attention to the quality of the products and improve their performance while ensuring the overall quality.
We can provide steel jaw cable puller with wire diameter ranging from 2.03mm to 45.7mm and from 0.68 tons to 9 tons. Contact us to get the best price.
We can currently produce a variety of high-performance alloy steels that can be used for wire diameters between 0.08~1.8in (2.03~45.7mm), tensions between 1500~20000lbs (0.68~9tons) and for various wire types of Jaw Cable Gripper.
Steel Wire Rope Gripper is made of high-performance alloy steel by hot die forging. It has a variety of styles to suit more wires.
HULK Metal offers a versatile range of Jaw Grip Puller for Aluminum Cable models, from lightweight wire grip pullers to heavy-duty cable pulling tools. With OEM customization, advanced production lines, and stringent quality controls, we ensure performance, durability, and after-sale support.
ABC Conductor Grips are special tools designed for ABC wire pulling, tightening and other working environments. Its clamp can better protect the ABC when pulling. We offer a variety of ABC Conductor Grips. Contact us for better prices.
The Jaw Rope Puller is designed for tensioning and routing ropes, cables, wire ropes, etc. We can currently provide Jaw Rope Pullers with clamping wire diameters ranging from 1.9mm to 45.7mm and pulling forces ranging from 1500 to 20000LBS.
Jaw Wire Puller orders will undergo strict sampling inspections before leaving the factory to ensure that the order qualification rate can reach 99.99%. We provide QA services. You can purchase with confidence.
Guy wire jaw grip puller is a tool designed to clamp wires and provide a fulcrum for tensioning them. It is simple to operate and can protect the wires while providing a stronger clamping force. We are a Chinese factory and can provide products with higher cost performance.

As a top metalworking service provider, we want to let every customer experience a sense of security in purchasing, sales, etc., and better realize their value through continuously defining new standards for products and services.
Room 901, Intelligent Park A Building, No. 86 ChunYang Rd, Qingdao, China 266109
© 2025 HULK Metal All Rights Reserved. All Rights Reserved.




 EN
EN RU
RU