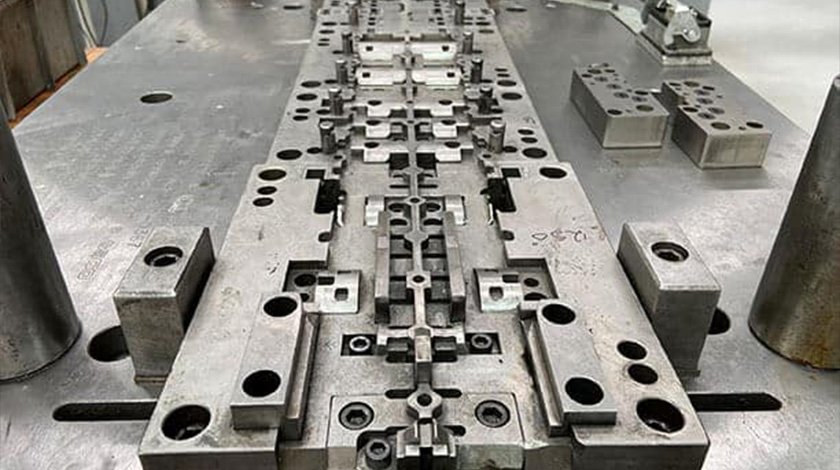
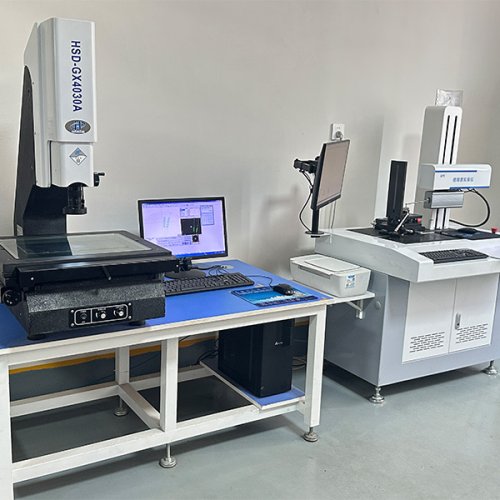
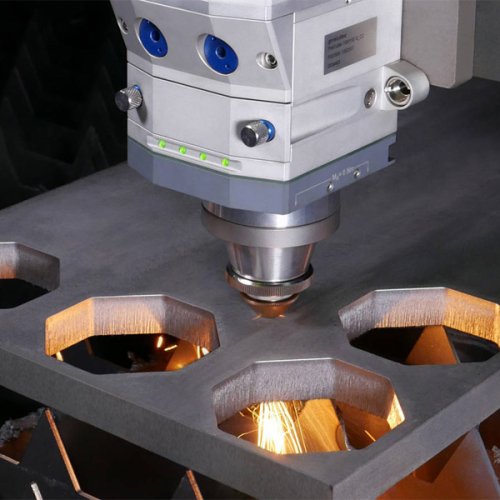
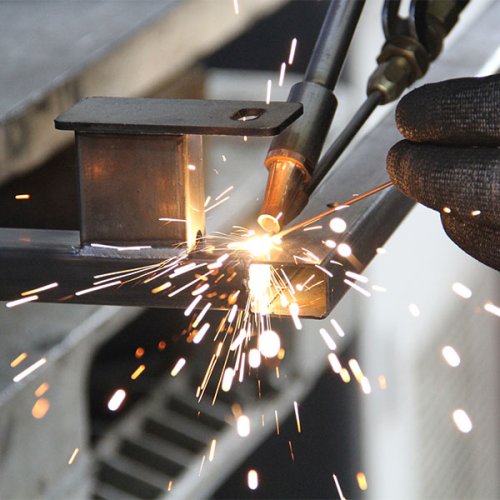
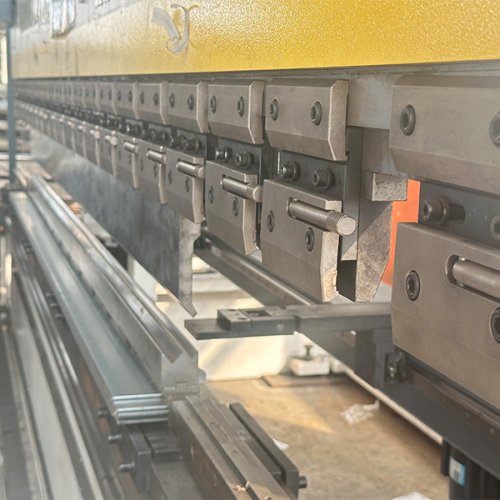
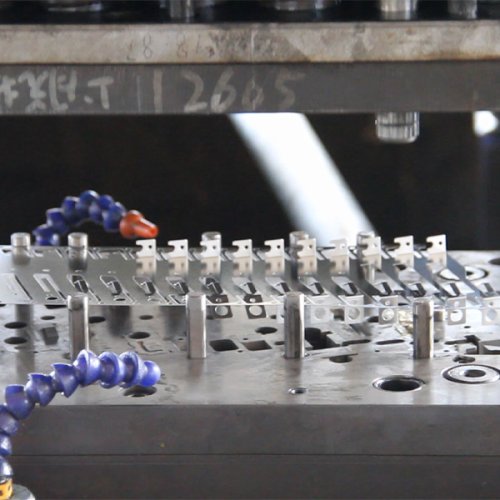
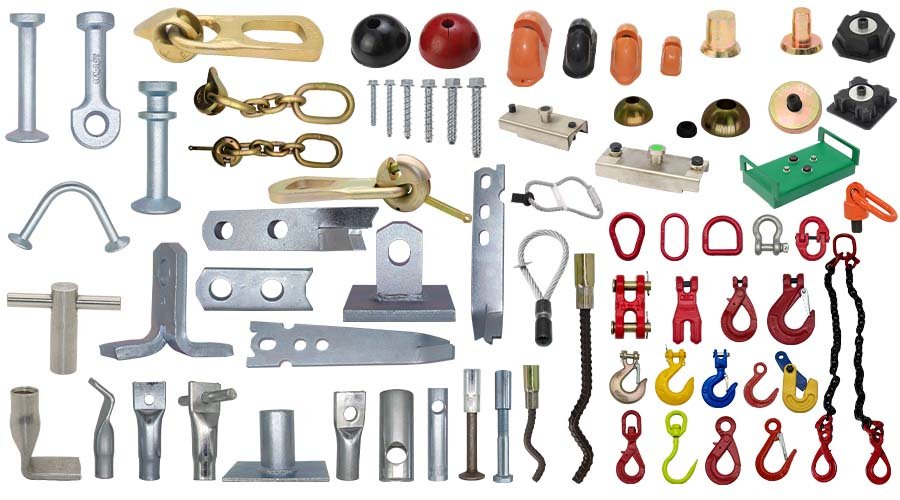
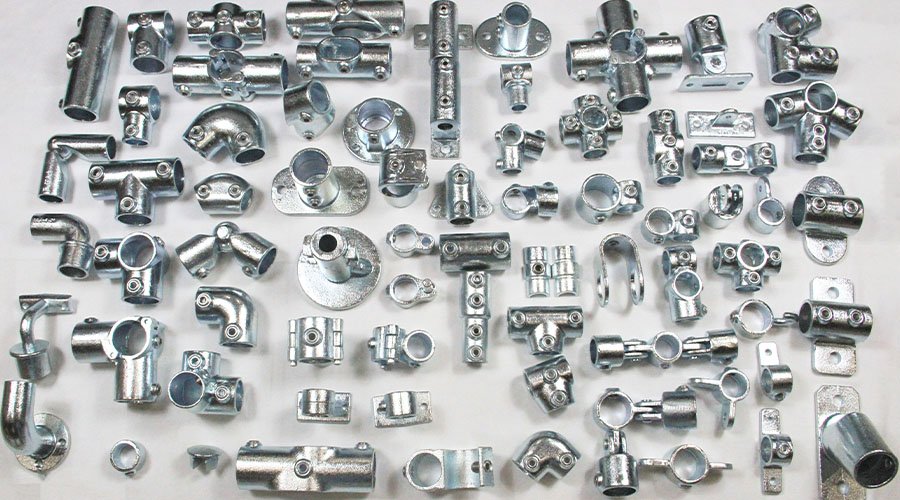
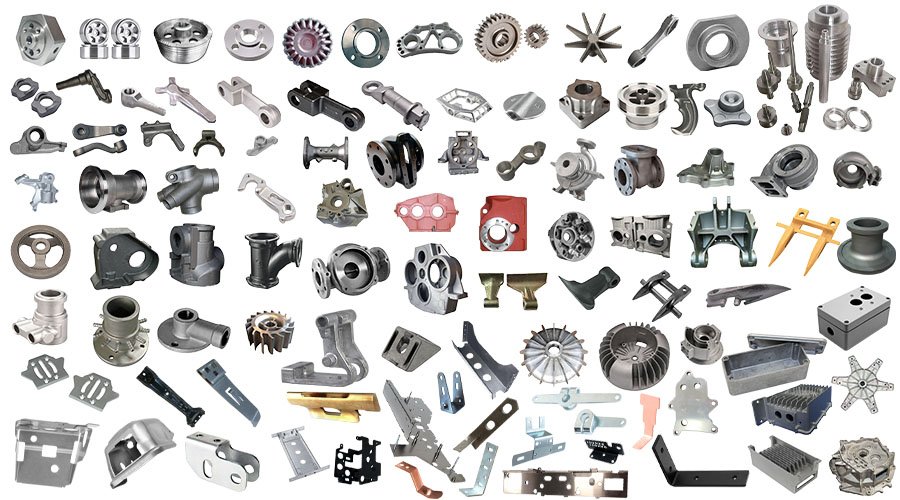
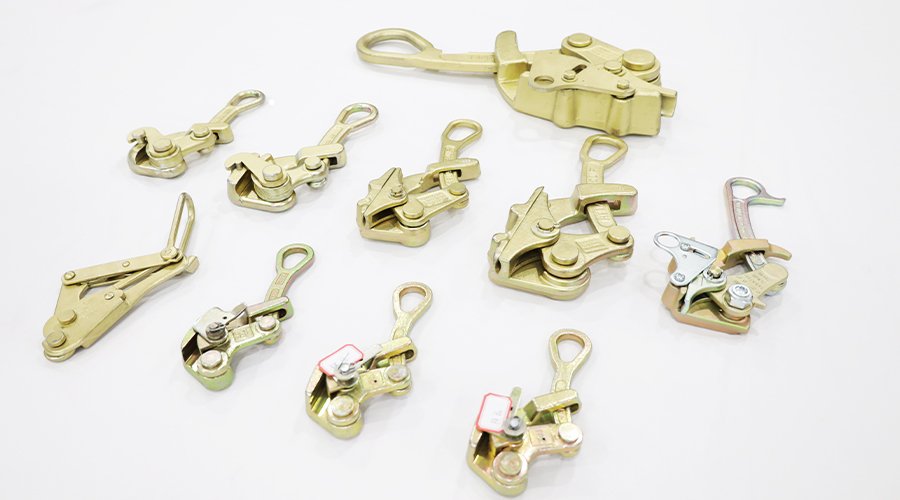
Metal stamping parts include a wide range of components such as brackets, clips, washers, terminals, housings, and panels. These parts serve crucial roles in automotive, electronics, appliances, and industrial machinery applications. Customized stamping parts can be produced in various metals like steel, aluminum, and copper alloys, offering high durability and precise tolerances. Our expertise ensures parts meet strict specifications, enhancing overall product performance and reliability in demanding environments.

 EN
EN RU
RU